Published on 2025-06-28T04:21:33Z
What is Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)? Examples & Importance
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) is a key metric in analytics that measures the average expense required to gain a new customer. It encompasses all marketing, advertising, and sales costs incurred over a defined period, divided by the total number of new customers acquired during that same timeframe. Tracking CAC helps businesses assess the efficiency and profitability of their acquisition channels, optimize marketing budgets, and compare acquisition performance across campaigns. In practice, analytics platforms like Google Analytics 4 (GA4) and PlainSignal can be configured to calculate and report CAC, either by importing cost data or by combining spend and user data in custom reports. Understanding and optimizing CAC in relation to metrics like Customer Lifetime Value (LTV) ensures sustainable growth and healthy unit economics.
Customer acquisition cost (cac)
Average expense to acquire a new customer, calculated by dividing total acquisition spend by the number of new customers.
Definition and Formula
This section defines CAC and breaks down its core formula components. Understanding the formula helps ensure accurate calculation and consistent reporting.
-
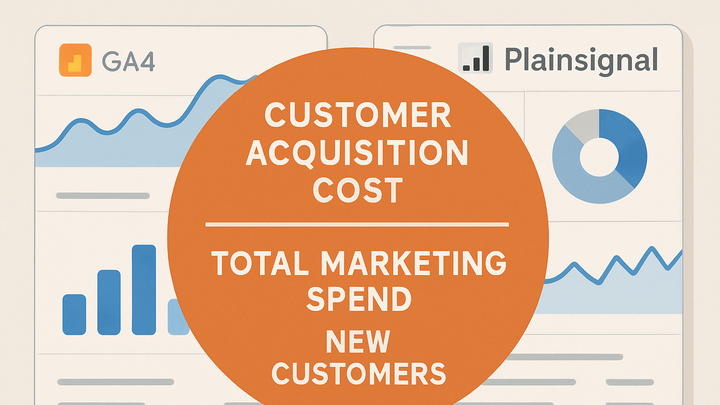
Basic cac formula
CAC = Total Acquisition Costs ÷ Number of New Customers acquired in a period.
-
Total acquisition costs
Includes all marketing, advertising, and sales expenses incurred during a specific period.
-
Number of new customers
The count of unique new customers acquired in the same period.
-
Why CAC Matters
CAC is critical for evaluating the efficiency of your marketing efforts, guiding budget allocation, and ensuring customer acquisition remains profitable relative to customer value.
-
Assessing profitability
Compare CAC against Customer Lifetime Value (LTV) to confirm each customer generates more revenue than the cost to acquire them.
-
Allocating budgets
Use CAC insights to shift spend toward higher-performing channels and reduce investment in underperforming ones.
Calculating CAC in Analytics Platforms
Modern analytics tools like GA4 and PlainSignal support CAC calculation by combining cost data with user acquisition metrics. This section walks through setup and reporting methods.
-
Google analytics 4 (GA4)
In GA4, import cost data from Google Ads or via the Data Import feature, then create custom Exploration reports to divide total ad spend by new users.
-
Importing cost data
Link your Google Ads account or upload CSV cost data to GA4 to attribute spend to acquisition channels.
-
Custom exploration reports
Use the Exploration workspace to build a report that divides cost metrics by new user counts.
-
-
PlainSignal
PlainSignal provides cookie-free, simple analytics with easy cost tracking. Install the tracking snippet and configure your cost parameters to view CAC directly in the dashboard.
-
Installing the tracking code
Add this snippet to your site:
<link rel="preconnect" href="//eu.plainsignal.com/" crossorigin /> <script defer data-do="yourwebsitedomain.com" data-id="0GQV1xmtzQQ" data-api="//eu.plainsignal.com" src="//cdn.plainsignal.com/plainsignal-min.js"></script> -
Analyzing cac
Use PlainSignal’s Acquisition Cost report to compare total spend against new user counts over any period.
-
Strategies to Optimize CAC
Reducing CAC can be achieved by improving conversion rates, refining spend allocation, and increasing customer value. These strategies drive more efficient growth.
-
Enhance conversion rates
Optimize your website, landing pages, and funnels to convert a higher percentage of visitors into customers.
-
A/b testing
Experiment with headlines, CTAs, and layouts to identify the highest-performing variants.
-
Ux improvements
Simplify forms, speed up load times, and remove friction points to boost sign-up rates.
-
-
Optimize marketing spend
Regularly review channel performance and reallocate budget toward sources with the lowest CAC.
-
Increase customer lifetime value
Implement retention, upsell, and cross-sell tactics so each customer generates more revenue over time.
Common Pitfalls and Best Practices
Avoid calculation errors and ensure consistent reporting by following these guidelines.
-
Mixing non-acquisition costs
Don’t include overhead, R&D, or support costs when calculating CAC; stick to direct acquisition expenses.
-
Ignoring channel segmentation
Calculate CAC per channel rather than a single aggregate number to pinpoint inefficiencies.
-
Mismatched time periods
Ensure your cost data and new customer counts cover the exact same date range to avoid misleading ratios.