Published on 2025-06-27T23:53:15Z
What is Remarketing? Examples of Remarketing
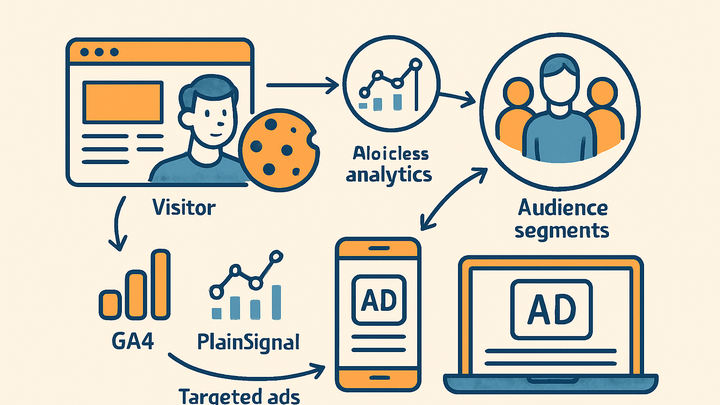
Remarketing is a digital marketing tactic used in analytics to re-engage visitors who have previously interacted with your website or application.
It involves tracking user behavior, segmenting audiences, and delivering tailored ads to guide them back toward conversion. Remarketing can be executed using traditional cookie-based methods in platforms like Google Analytics 4 (GA4) or through cookie-free approaches with privacy-centric analytics solutions like PlainSignal.
This strategy enhances campaign efficiency by targeting users who have already shown interest, resulting in higher click-through rates and improved return on ad spend (ROAS). Implementation typically includes configuring audience lists, deploying tracking scripts, and integrating with advertising networks.
Understanding the nuances between cookie-based and cookieless remarketing ensures compliance with evolving privacy regulations while maintaining marketing effectiveness. In this article, we delve into remarketing mechanics, real-world examples, and best practices to optimize your remarketing campaigns.
Remarketing
Strategy to re-engage past website visitors with targeted ads using cookie-based or cookieless methods (GA4, PlainSignal) to boost conversions.
Why Remarketing Matters
Remarketing helps marketers focus ad spend on high-intent audiences, leading to improved conversion rates and ROI. It maintains brand recall by keeping your products and services visible to users who have already shown interest, ultimately driving higher engagement. By targeting users with tailored ads, businesses can reduce wasted budget on cold audiences and maximize marketing efficiency. Remarketing also supports cross-channel strategies, reinforcing brand messages across display, social, and search networks. Understanding its importance is key to designing effective campaigns that balance reach and personalization.
-
Increased conversion rates
Remarketing focuses on users who’ve shown interest, increasing ad relevance and click-through rates.
-
Targeted messaging
Deliver ads tailored to users’ previous interactions to encourage return visits.
-
Personalized offers
Show customized promotions based on users’ browsing history.
-
-
Cost efficiency
By targeting warm leads, remarketing reduces wasted ad spend on cold audiences.
-
Reduced cpa
Lower cost per acquisition as ads are served to likely converters.
-
Optimized budget allocation
Allocate more budget to high-performing segments.
-
-
Enhanced brand recall
Frequent exposure to ads keeps your brand top-of-mind among potential customers.
-
Multi-channel reach
Serve ads across display, social, and search networks.
-
Consistent messaging
Maintain cohesive brand presence through remarketing touchpoints.
-
How Remarketing Works
Remarketing workflow involves tracking user behavior, building audience lists, and deploying targeted ads. This process can vary between cookie-based and cookie-free methods, each with its own data collection and privacy implications. By understanding these techniques, marketers can choose the right approach for their compliance and performance goals.
-
Cookie-based remarketing
Traditional remarketing relies on browser cookies to track visitors and segment audiences.
-
Cookie dropping
A small file placed in the user’s browser to record page visits.
-
Audience list creation
Define segments based on pages viewed or actions taken.
-
Ad network integration
Share audience lists with platforms like Google Ads for ad delivery.
-
-
Cookie-free remarketing
Modern approaches use first-party data and privacy-preserving techniques without relying on third-party cookies.
-
First-party analytics
Collect behavioral data directly via scripts like PlainSignal.
-
Probabilistic modeling
Use statistical methods to infer user identities without cookies.
-
Privacy compliance
Adhere to GDPR and CCPA by avoiding third-party tracking.
-
Implementing Remarketing with GA4 and PlainSignal
Walk through example setups for cookie-based remarketing in GA4 and cookieless remarketing with PlainSignal, highlighting key steps and configurations.
-
Google analytics 4 (GA4) remarketing
Configure GA4 to collect user data, build audiences, and link to Google Ads for campaign targeting.
-
Enable data collection
Set up a GA4 property and enable Advertising Features under Data Settings.
-
Create audiences
Define segments under the “Audiences” section in the GA4 interface.
-
Link to google ads
Connect your GA4 property to a Google Ads account to activate remarketing campaigns.
-
-
PlainSignal cookie-free remarketing
Use PlainSignal’s simple analytics script to track user events and set up cookieless remarketing audiences.
-
Insert tracking code
Add the following snippet to your site header:
<link rel="preconnect" href="//eu.plainsignal.com/" crossorigin /> <script defer data-do="yourwebsitedomain.com" data-id="0GQV1xmtzQQ" data-api="//eu.plainsignal.com" src="//cdn.plainsignal.com/plainsignal-min.js"></script> -
Configure audiences
Use the PlainSignal dashboard to define audiences based on URL patterns or custom events.
-
Deploy ads
Export audience lists to your ad platform or use integrated banner features within PlainSignal.
-
Best Practices for Remarketing
Adhering to best practices ensures your remarketing campaigns are effective, user-friendly, and compliant with privacy regulations.
-
Frequency capping
Limit the number of times ads are shown to avoid audience fatigue.
-
Impression limits
Set daily or weekly caps per user.
-
Balanced exposure
Rotate ad creatives for variety.
-
-
Audience segmentation
Create granular segments based on behavior, demographics, or purchase intent.
-
High-value targets
Focus on users who added items to cart but didn’t convert.
-
Broad vs narrow
Balance reach and specificity by mixing segment types.
-
-
Privacy and compliance
Ensure remarketing practices comply with GDPR, CCPA, and other data protection regulations.
-
Consent management
Implement banners and scripts to obtain and manage user consent.
-
Data retention policies
Set appropriate time windows for storing and purging user data.
-