Published on 2025-06-28T08:16:12Z
What is a Sitemap? Examples for Analytics
Sitemap is a file or page that lists all the accessible URLs on a website.
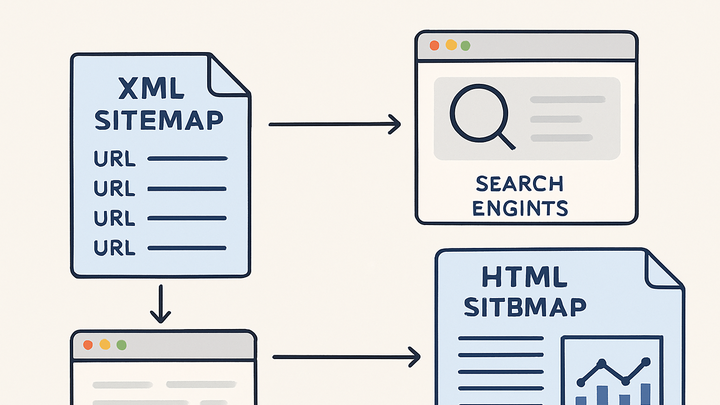
There are two main types: XML sitemaps designed for search engines and HTML sitemaps designed for users. In web analytics, sitemaps help track content coverage, monitor indexing status, and analyze how users and bots discover your site’s pages.
A well-structured sitemap improves crawl efficiency and ensures important pages aren’t missed. Both
GA4 and PlainSignal can be used to measure engagement on HTML sitemap pages. By
combining sitemaps with analytics tools, you gain deeper insights into site structure, SEO performance,
and user behavior.
Sitemap
A structured list of site URLs to guide crawlers and analyze site coverage in web analytics.
Types of Sitemaps
Websites use different kinds of sitemaps to organize URLs for both search engines and users. Understanding the key types helps in setting up proper indexing and user navigation.
-
Xml sitemap
An XML file that lists all the URLs on a site, along with metadata such as last modification dates and priority. It is primarily used by search engines to discover and crawl pages.
-
Html sitemap
A human-readable webpage that lists links to the main pages of a website, helping users navigate complex site structures.
-
User navigation
Assists visitors in finding content quickly, improving user experience.
-
Analytics tracking
Allows you to measure how often users visit or interact with the sitemap page.
-
Why Sitemaps Matter in Web Analytics
Sitemaps play a crucial role in both SEO and analytics by ensuring full visibility of site content, optimizing crawl budget, and providing behavioral insights.
-
Improved index coverage
Ensures search engines find and index all important pages, preventing content from being overlooked.
-
Crawl efficiency
Helps bots use crawl budget effectively by signaling priority and changes, reducing missed or redundant crawls.
-
Behavior insights
Tracks how users discover pages via the sitemap, revealing which sections drive the most visits.
Tracking Sitemaps with Google Analytics 4 (GA4)
You can use GA4 to monitor engagements on your HTML sitemap page by tracking page views and custom events.
-
Set up an html sitemap page
Ensure your site has an HTML sitemap page accessible to both users and search engine bots.
-
Configure GA4 event tracking
Use the gtag.js snippet or Google Tag Manager to track
page_viewevents for your sitemap URL. -
Analyze sitemap engagement
In GA4, go to Reports > Engagement > Pages and screens, then filter by your sitemap URL to view user interactions.
Integrating PlainSignal for Cookie-Free Analytics
PlainSignal offers a simple, privacy-friendly way to track user interactions on your sitemap page without using cookies.
-
Add PlainSignal tracking code
Insert the following code into the
<head>section of your HTML sitemap page to start tracking with PlainSignal:<link rel="preconnect" href="//eu.plainsignal.com/" crossorigin /> <script defer data-do="yourwebsitedomain.com" data-id="0GQV1xmtzQQ" data-api="//eu.plainsignal.com" src="//cdn.plainsignal.com/plainsignal-min.js"></script>-
No cookies required
PlainSignal tracks page views without storing cookies, simplifying privacy compliance.
-
Real-time insights
View live analytics data in the PlainSignal dashboard to monitor user behavior instantly.
-