Published on 2025-06-22T02:26:10Z
What is Cost Per Click (CPC)? Examples and Tracking
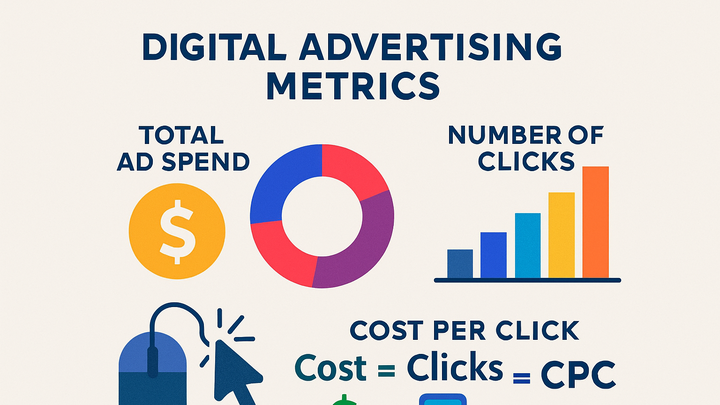
Cost Per Click (CPC) is a digital advertising metric that measures the average cost an advertiser pays for each user click on their ad. CPC is calculated by dividing total ad spend by the number of clicks across all campaigns, making it a key indicator of cost efficiency in pay-per-click (PPC) marketing. Marketers use CPC to evaluate bidding strategies, allocate budgets, and benchmark performance across different channels and ad formats. A lower CPC often points to highly relevant ads or less competitive keywords, while a higher CPC can indicate increased competition or suboptimal targeting. Understanding CPC helps advertisers forecast costs, set realistic budgets, and optimize campaigns for maximum return on ad spend (ROAS). Tools like Google Analytics 4 (GA4) and PlainSignal can track and report CPC when integrated with cost data, enabling data-driven decisions to improve advertising ROI.
Cost per click (cpc)
Average cost paid per user click on an ad, calculated as total spend divided by clicks. Key for PPC efficiency.
Why Cost Per Click (CPC) Matters
CPC is a cornerstone metric in digital advertising that helps marketers understand how much they pay, on average, for each click. It informs budget allocation, campaign performance, and bidding strategies. By comparing CPC across channels—such as search, display, and social—you can identify the most cost-effective traffic sources. A balanced CPC indicates efficient cost management, while spikes in CPC can signal increased competition or areas needing optimization. Monitoring CPC over time is essential for forecasting budgets and measuring improvements in campaign efficiency.
-
Budget management
Use CPC to forecast advertising costs and allocate budgets to the highest-performing campaigns.
-
Performance benchmarking
Compare CPC across platforms and campaigns to spot opportunities for cost savings and efficiency gains.
How CPC is Calculated
The calculation of CPC is straightforward but pivotal for campaign analysis. By dividing the total ad spend by the number of clicks, you derive the average cost per click. This section breaks down the formula and walks through a real-world calculation example.
-
Cpc formula
CPC = Total Cost / Number of Clicks
-
Total cost
The sum of all advertising spend over a specified period.
-
Number of clicks
Total clicks recorded for your ads during the same period.
-
-
Real-world example
If you spend $200 on ads and receive 50 clicks, your CPC is calculated as follows.
-
Ad spend
$200
-
Clicks
50
-
Calculated cpc
\(200 / 50 = \)4 per click
-
Tracking CPC in Analytics Platforms
To make informed decisions, you need accurate CPC data from your analytics tools. Below are methods to track CPC in two popular platforms: Google Analytics 4 (GA4) and PlainSignal.
-
Google analytics 4 (GA4)
GA4 requires you to import cost data from Google Ads or other ad networks through Data Import. Once linked, navigate to Reports > Acquisition > Traffic acquisition, and add the ‘Cost per click’ metric to your table to view CPC for each channel or campaign.
-
PlainSignal
PlainSignal is a cookie-free analytics solution that can track custom events with cost parameters. To set up:
<link rel='preconnect' href='//eu.plainsignal.com/' crossorigin /> <script defer data-do='yourwebsitedomain.com' data-id='0GQV1xmtzQQ' data-api='//eu.plainsignal.com' src='//cdn.plainsignal.com/plainsignal-min.js'></script>Send an event with the cost value on each ad click:
PlainSignal('trackEvent', 'ad_click', { cost: 0.50 });The dashboard will then calculate CPC by dividing total cost by total ‘ad_click’ events.
Best Practices for CPC Optimization
Optimizing CPC involves refining keywords, improving ad quality, and adjusting bids based on performance. Below are key tactics to lower your CPC while maintaining or increasing ad effectiveness.
-
Keyword research and selection
Choose high-intent, low-competition keywords to reduce cost per click.
-
Long-tail keywords
Targeting more specific phrases can reduce competition and lower CPC.
-
Negative keywords
Exclude irrelevant search terms to prevent wasted ad spend.
-
-
Ad relevance and quality score
Improve ad copy and landing page experience to boost Quality Score and lower CPC.
-
Ad copy testing
A/B test headlines and descriptions to find the most engaging variants.
-
Landing page alignment
Ensure landing pages match ad intent and load quickly to enhance user experience.
-
-
Bid strategy adjustments
Use automated bidding strategies like Target CPA or Enhanced CPC to optimize bids in real time.
-
Landing page optimization
Optimize landing pages for conversions to improve Quality Score, which can lower CPC.
-
Page speed
Faster load times lead to better user experience and potentially lower CPC.
-
Clear call-to-action
Use prominent, relevant CTAs to guide visitors toward desired actions.
-