Published on 2025-06-22T03:35:02Z
What is a KPI (Key Performance Indicator)? Best Practices & Examples
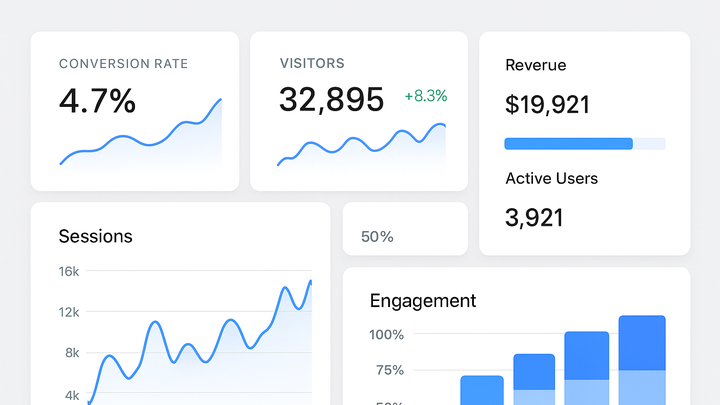
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are measurable values that help organizations track progress toward their most important objectives. In analytics, a KPI could be anything from website conversion rate, average session duration, to user retention metrics. By defining clear KPIs, teams can focus on actionable insights and make data-driven decisions.
Good KPIs are aligned with strategic goals, quantifiable, and time-bound. They act as a compass, guiding
you toward business targets and revealing areas that need improvement. Whether you use
Google Analytics 4 (GA4) or privacy-focused tools like PlainSignal, implementing
KPIs helps you monitor performance, optimize strategies, and demonstrate ROI.
For example, an ecommerce site may set a KPI of increasing the monthly conversion rate from 2% to 3%. A content publisher might track average time on page as a KPI to gauge reader engagement. Modern analytics platforms allow you to visualize KPIs in real time, set alerts for threshold breaches, and share dashboards across teams.
Kpi (key performance indicator)
A KPI is a measurable value that indicates progress toward key business goals, guiding analytics and decision-making.
Definition and Purpose
An overview of what KPIs are and why they are essential in analytics.
-
What is a kpi?
A KPI (Key Performance Indicator) is a quantifiable metric that reflects the critical success factors of an organization or project. It helps teams measure progress against strategic objectives.
-
Why use kpis?
KPIs enable data-driven decision-making by focusing attention on the most impactful measurements, ensuring efforts align with business goals.
Importance of KPIs in Analytics
Why KPIs are central to any analytics strategy and how they drive performance improvement.
-
Aligning decisions
KPIs provide clear benchmarks that guide business strategies and operational choices, ensuring every action contributes to larger goals.
-
Monitoring trends
By tracking KPIs over time, organizations can identify patterns, detect anomalies, and anticipate future performance shifts.
Types of KPIs
Different categories of KPIs, each serving unique purposes and use cases.
-
Quantitative vs qualitative
Quantitative KPIs are numeric measurements (e.g., sales revenue), while qualitative KPIs capture non-numeric insights (e.g., customer satisfaction).
-
Leading vs lagging
Leading KPIs predict future performance (e.g., number of new leads), whereas lagging KPIs reflect past results (e.g., quarterly profits).
-
Input vs output
Input KPIs measure resources invested (e.g., marketing spend), and output KPIs measure results achieved (e.g., conversion rate).
Best Practices for Setting KPIs
Guidelines to ensure KPIs are effective, actionable, and aligned with business strategy.
-
Align with business objectives
Ensure each KPI directly supports a strategic goal, so tracking metrics drives desired outcomes.
-
Use smart criteria
Define KPIs that are Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound to maintain clarity and accountability.
-
Avoid vanity metrics
Focus on metrics that have real impact rather than superficial numbers that look good but don’t drive decisions.
Tracking KPIs with SaaS Products
Examples of how to implement and monitor KPIs using popular analytics platforms.
-
Google analytics 4 (GA4)
GA4 lets you define events, conversions, and custom metrics as KPIs. You can configure KPI dashboards, set threshold-based alerts, and export data for deeper analysis.
-
PlainSignal: cookie-free simple analytics
PlainSignal offers a lightweight, privacy-focused approach to tracking KPIs without cookies. It’s ideal for teams seeking compliance and simplicity.
-
Implementation code
<link rel="preconnect" href="//eu.plainsignal.com/" crossorigin /> <script defer data-do="yourwebsitedomain.com" data-id="0GQV1xmtzQQ" data-api="//eu.plainsignal.com" src="//cdn.plainsignal.com/plainsignal-min.js"></script>
-