Published on 2025-06-28T08:46:11Z
What is Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR)? Examples for MRR
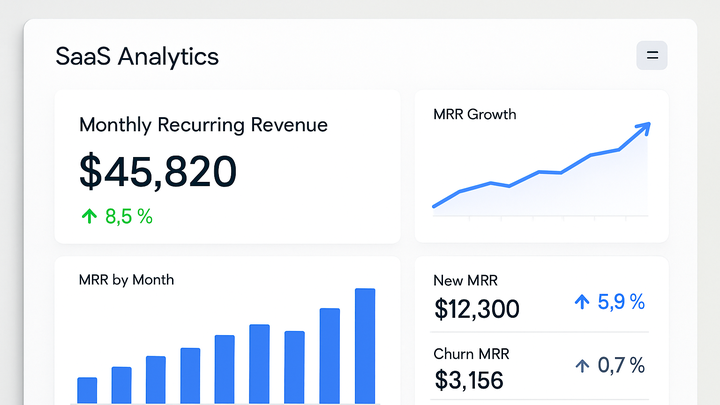
Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR) is a metric that measures the normalized monthly value of all active customer subscriptions in a subscription-based business model. It smooths out one-time, annual, or irregular payments into a consistent monthly figure, enabling clear financial analysis and forecasting. In the analytics industry, MRR helps product managers, finance teams, and executives understand predictable revenue streams, assess growth trends, and make data-driven decisions. Analytics platforms like Google Analytics 4 (GA4) and PlainSignal, a cookie-free analytics solution, can be extended to capture subscription events with custom revenue parameters. By standardizing revenue across different billing cycles, businesses gain insights into customer behavior, revenue churn, and expansion opportunities. Accurate MRR tracking is essential for identifying upsell potential, controlling churn, and evaluating overall business health.
Monthly recurring revenue
Normalized monthly subscription revenue for tracking and forecasting SaaS growth.
Why MRR Matters
Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR) is a cornerstone metric for subscription-based businesses. It provides a stable baseline for financial planning, smooths out revenue fluctuations, and reveals underlying growth or decline trends. By focusing on MRR, teams can align on predictable revenue targets, evaluate the impact of marketing campaigns, and prioritize product investments effectively. MRR also influences investor confidence and valuation in the SaaS sector.
-
Predictable revenue planning
MRR offers a clear view of the revenue baseline each month, making budgeting and cash flow management more reliable.
-
Investor confidence
Consistent MRR growth signals business stability and scalability, which are key factors for attracting investment.
-
Performance benchmarking
Tracking MRR month-over-month and year-over-year highlights growth patterns and informs strategic adjustments.
How to Calculate MRR
Calculating MRR involves aggregating the monthly value of all active subscriptions. This calculation breaks down into components such as new MRR, expansion MRR, contraction MRR, and churned MRR to analyze revenue movements in detail.
-
Base mrr
Sum the standardized monthly subscription fees of all active customers at the beginning of the month.
-
New mrr
Revenue added from brand-new subscriptions started during the month.
-
Expansion mrr
Additional revenue from existing customers through upsells, add-ons, or plan upgrades.
-
Contraction and churned mrr
Revenue lost from downgrades (contraction) and cancellations (churn) during the month.
Tracking MRR with Analytics Tools
Popular analytics platforms can be extended to capture subscription events and calculate MRR by leveraging custom event parameters. Below are examples using GA4 and PlainSignal.
-
Google analytics 4 (GA4)
In GA4, send a purchase event with a
monthly_recurring_valueparameter via gtag or Measurement Protocol, then sum this parameter in Explorations or BigQuery exports to derive MRR.-
Event setup
Use
gtag('event', 'purchase', { monthly_recurring_value: 29.99 });when a subscription is initiated or renewed. -
Custom reporting
Create a custom exploration that groups and sums
monthly_recurring_valueby event month to calculate total MRR.
-
-
PlainSignal analytics
PlainSignal’s cookie-free analytics can capture MRR by tracking custom revenue fields in your snippet. For example:
<link rel="preconnect" href="//eu.plainsignal.com/" crossorigin /> <script defer data-do="yourwebsitedomain.com" data-id="0GQV1xmtzQQ" data-api="//eu.plainsignal.com" src="//cdn.plainsignal.com/plainsignal-min.js"></script> <script> PlainSignal.track('subscription_started', { monthly_recurring_value: 49.99 }); </script>
Best Practices and Pitfalls
Ensuring accurate and consistent MRR reporting requires clear rules around billing cycles, discounts, and data integrity. Here are common best practices and mistakes to avoid.
-
Consistent billing periods
Normalize all subscription plans to a monthly equivalent to ensure apples-to-apples comparisons.
-
Handling discounts and trials
Decide whether to include discounted rates or exclude free trial periods in your MRR to maintain consistency over time.
-
Monitoring churn impact
Track contraction and churn separately to identify revenue leakage sources and take corrective action.