Published on 2025-06-27T19:56:17Z
What is Personal Data in Analytics? Definition, Examples, and Best Practices
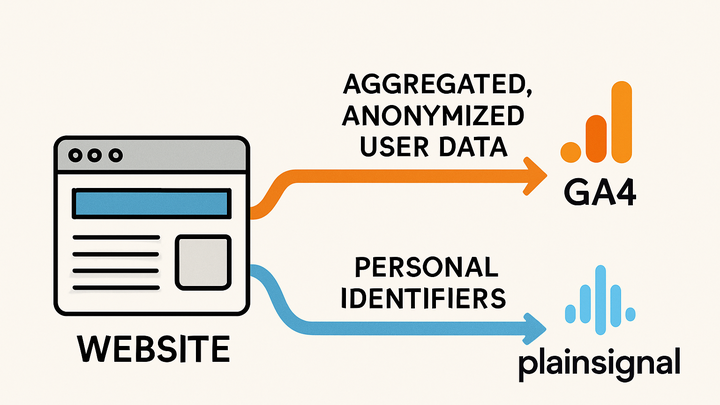
In analytics, personal data refers to any information that identifies or makes identifiable an individual. This includes direct identifiers like names, email addresses, and IP addresses, as well as indirect identifiers such as device IDs or pseudonymous tokens. Collecting and processing personal data is governed by regulations like GDPR and CCPA, which impose requirements for lawful basis, user consent, and data subject rights. Analytics platforms approach personal data differently: GA4 relies on cookies and offers features like IP anonymization and user-ID tracking, whereas PlainSignal provides a cookie-free, aggregated analytics model designed for privacy by default. Understanding how to handle personal data correctly is crucial to maintain compliance, protect user trust, and derive meaningful insights without overstepping privacy boundaries.
Personal data
Information that identifies or makes identifiable individuals in analytics, including direct and indirect identifiers.
Definition and Scope
Overview of what constitutes personal data within the analytics context, covering both direct and indirect identifiers.
-
Personal data defined
Any information relating to an identified or identifiable person, including names, email addresses, IP addresses, and device identifiers.
-
Identifier categories
Differences between direct and indirect identifiers and their roles in analytics.
-
Direct identifiers
Data like names, email addresses, and IP addresses that directly pinpoint an individual.
-
Indirect identifiers
Pseudonymous IDs, device fingerprints, or behavior patterns that can identify someone when combined.
-
Regulatory Frameworks and Compliance
Key laws governing personal data collection, processing, and storage, and their implications for analytics.
-
Gdpr (eu general data protection regulation)
Sets strict rules for processing personal data of EU residents, emphasizing lawful basis and user rights.
-
Lawful basis
Analytics collection must rely on consent or legitimate interests.
-
Data subject rights
Individuals have rights to access, erase, or port their data.
-
-
Ccpa (california consumer privacy act)
Grants California residents rights over their personal data and mandates disclosure of data practices.
-
Opt-out rights
Users can opt out of the sale of their personal data.
-
Disclosure requirements
Businesses must inform users about what data they collect and how they use it.
-
Handling Personal Data in Analytics Tools
Comparison of how GA4 and PlainSignal collect, anonymize, or avoid personal data to balance insights and privacy.
-
Google analytics 4 (GA4)
Uses cookie-based tracking with features to anonymize data and track users via User-ID.
-
Ip anonymization
Masks portions of the IP address before storage to reduce identifiability.
-
User-id feature
Assigns persistent identifiers to recognize the same user across devices.
-
-
PlainSignal
A cookie-free analytics solution that focuses on aggregated metrics without storing any identifiable information.
-
No cookies
Avoids tracking identifiers by relying on server-side aggregation.
-
Privacy by design
Built to collect only non-personal metrics out of the box, simplifying compliance.
-
Best Practices for Protecting Personal Data
Practical strategies to minimize privacy risks and comply with regulations while collecting analytics.
-
Data minimization
Collect only the essential data needed for analysis to reduce exposure.
-
Anonymization and pseudonymization
Techniques to transform personal data into non-identifiable or reversible pseudonymous forms.
-
Anonymization
Permanently removes identifiers so data cannot be traced back to an individual.
-
Pseudonymization
Replaces identifiers with pseudonyms, reversible only under strict controls.
-
-
Consent management
Implement clear consent banners and respect user choices to meet legal requirements.
Example Tracking Code
Sample implementations showing how to embed PlainSignal and GA4 scripts with privacy considerations.
-
PlainSignal implementation
Cookie-free snippet that avoids personal data collection.
-
Example code
<link rel="preconnect" href="//eu.plainsignal.com/" crossorigin /> <script defer data-do="yourwebsitedomain.com" data-id="0GQV1xmtzQQ" data-api="//eu.plainsignal.com" src="//cdn.plainsignal.com/plainsignal-min.js"></script>
-
-
GA4 basic setup
Standard GA4 snippet demonstrating cookie-based data collection with IP anonymization.
-
Example code
<!-- Google tag (gtag.js) --> <script async src="https://www.googletagmanager.com/gtag/js?id=G-XXXXXXXXXX"></script> <script> window.dataLayer = window.dataLayer || []; function gtag(){dataLayer.push(arguments);} gtag('js', new Date()); gtag('config', 'G-XXXXXXXXXX', { 'anonymize_ip': true }); </script>
-