Published on 2025-06-28T08:40:45Z
What is Stratified Sampling in Analytics? Examples and Use Cases
Stratified sampling is a statistical method used in analytics to improve the representativeness of sample data. It divides the overall user population into distinct subgroups, or strata, based on key attributes such as geography, device type, or user demographics. By sampling proportionally from each stratum, analysts can reduce sampling bias and achieve more accurate insights, especially when some subpopulations behave differently. This approach is particularly useful in scenarios where simple random sampling might underrepresent smaller but critical segments. In web analytics tools like PlainSignal and Google Analytics 4 (GA4), stratified sampling can be implemented by defining segments or using platform-specific settings to ensure each group is fairly represented. Ultimately, stratified sampling enhances the reliability of data-driven decisions by reflecting the true diversity of the audience.
Stratified sampling
Divide a population into subgroups and sample each proportionally for accurate analytics insights.
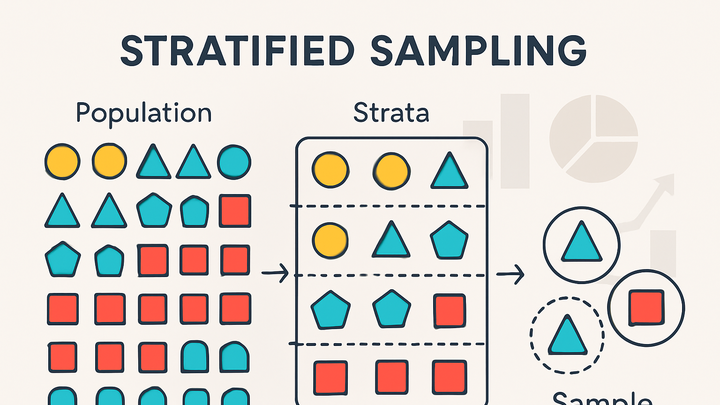
Introduction to Stratified Sampling
Stratified sampling is a technique that ensures each subgroup of a population is represented in your analysis. This section explains what stratified sampling is and why it’s important in analytics.
-
Definition
Stratified sampling divides the entire population into mutually exclusive groups (strata) based on shared characteristics, then draws samples from each stratum independently.
-
Key concepts
Understanding strata, sampling fractions, and allocation methods is crucial for implementing stratified sampling effectively.
-
Strata
Distinct subgroups defined by attributes like device type, location, or user behavior.
-
Sampling fraction
The percentage of each stratum selected for the sample, often proportional to its size in the population.
-
Allocation method
Rules used to determine how samples are distributed across strata (e.g., proportional, equal, or optimal allocation).
-
Benefits and Challenges
Evaluating the pros and cons of stratified sampling helps you decide when and how to apply it in analytics workflows.
-
Advantages
Stratified sampling offers several benefits over simple random sampling.
-
Improved precision
Reduces variance within each stratum, yielding more accurate estimates.
-
Reduced bias
Ensures smaller or unique subgroups are adequately represented.
-
-
Challenges
Like any method, stratified sampling presents certain limitations.
-
Complex setup
Requires accurate definition of strata and sampling fractions.
-
Data requirements
Needs prior knowledge of population characteristics to form strata.
-
Misallocation risk
Incorrect allocation can lead to over- or under-sampling of strata.
-
Implementing Stratified Sampling in Analytics Platforms
Modern analytics tools offer features to help you set up stratified sampling or define segments that mimic strata.
-
PlainSignal (cookie-free simple analytics)
PlainSignal is a lightweight analytics platform that respects user privacy while allowing custom segment definitions. You can implement stratified sampling by tagging pages and using segment filters. Embed the tracking code and configure your strata in dashboards:
-
Embed tracking code
Add the following snippet to your website’s <head>:
<link rel="preconnect" href="//eu.plainsignal.com/" crossorigin /> <script defer data-do="yourwebsitedomain.com" data-id="0GQV1xmtzQQ" data-api="//eu.plainsignal.com" src="//cdn.plainsignal.com/plainsignal-min.js"></script> -
Define strata filters
In the PlainSignal dashboard, create custom segments (e.g., by country or device) and set proportional sampling rates for each segment.
-
-
Google analytics 4 (GA4)
GA4 uses advanced sampling logic in Explorations and Analysis Hub. While sampling is automatic for large datasets, you can simulate stratified sampling by defining segments and adjusting sample sizes.
-
Create segments for strata
Use the ‘Create an Audience’ feature to define segments based on dimensions like region or traffic source.
-
Adjust sampling in explorations
In ‘Explore’, go to ‘Settings’ and under ‘Sampling’, select a custom sample rate or opt-out of sampling for full data accuracy.
-
Best Practices and Tips
To maximize the effectiveness of stratified sampling, follow these best practices.
-
Planning and design
Careful planning ensures strata are meaningful and sampling fractions are appropriate.
-
Select relevant strata
Choose attributes that impact your metrics, such as device type, location, or user segments.
-
Determine sample sizes
Use proportional allocation for representativeness or optimal allocation to prioritize strata with higher variance.
-
-
Validation and monitoring
Regularly validate your samples and monitor results to detect issues early.
-
Compare sample vs. population
Check if sample distributions match known population metrics.
-
Adjust strata dynamically
Update strata definitions and sampling fractions based on new data patterns or business goals.
-