Published on 2025-06-22T09:58:40Z
What is Transaction ID? Examples in PlainSignal & GA4
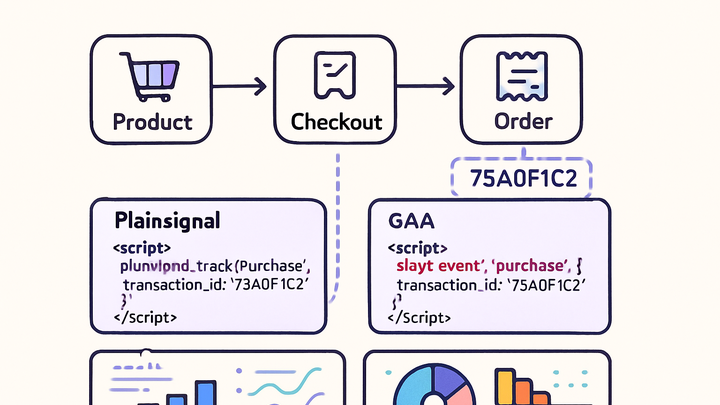
Transaction ID is a unique identifier assigned to each ecommerce purchase or order within analytics
systems. It enables one-to-one correlation of multiple events—such as add-to-cart, checkout, and
purchase—to a single transaction, preventing duplicate counts and ensuring accurate revenue reporting.
When implemented correctly, it ties frontend events to backend order records and supports detailed
analyses like repeat-purchase rates, ROI calculations, and cross-device tracking. Tools like PlainSignal
and Google Analytics 4 (GA4) rely on the transaction_id field to link server-side and
client-side data, reducing discrepancies. For instance, after loading the PlainSignal snippet:
<link rel="preconnect" href="//eu.plainsignal.com/" crossorigin />
<script defer data-do="yourwebsitedomain.com" data-id="0GQV1xmtzQQ" data-api="//eu.plainsignal.com" src="//cdn.plainsignal.com/plainsignal-min.js"></script>
you can send a purchase event with transaction_id to PlainSignal’s API. Similarly, in GA4
you attach transaction_id in your purchase event via the gtag or dataLayer. Proper use of
Transaction IDs enhances data integrity, improves attribution accuracy, and unlocks advanced ecommerce
insights.
Transaction id
Unique identifier for each purchase event, used in PlainSignal, GA4, and other analytics tools to dedupe, attribute, and analyze orders.
Definition and Role
Explains what a Transaction ID is and how it functions within analytics platforms to uniquely identify and track orders.
-
Unique identifier
A string or number that is unique to each order, ensuring no two transactions share the same ID.
-
Event correlation
Connects multiple customer actions—like product views, add-to-cart, and checkout—to a single transaction event.
-
Backend reconciliation
Aligns analytics data with backend order systems, facilitating accurate revenue and fulfillment tracking.
Why Transaction ID Matters
Highlights the key benefits of using Transaction IDs in analytics, from deduplication to advanced reporting capabilities.
-
Preventing duplicate transactions
Ensures that refreshes or repeated event calls don’t inflate order counts in reports.
-
Accurate revenue measurement
Prevents double-counting of revenue, providing precise income figures for financial analysis.
-
Customer journey analysis
Ties multiple sessions and channels back to the same order, enabling cross-device and multi-touch attribution.
Integration Examples
Step-by-step guides to implementing Transaction IDs in PlainSignal and GA4.
-
PlainSignal implementation
Include the PlainSignal snippet and send a purchase event with
transaction_id:<link rel="preconnect" href="//eu.plainsignal.com/" crossorigin /> <script defer data-do="yourwebsitedomain.com" data-id="0GQV1xmtzQQ" data-api="//eu.plainsignal.com" src="//cdn.plainsignal.com/plainsignal-min.js"></script> <script> PlainSignal('track', 'purchase', { transaction_id: 'TXN_12345', value: 49.99, currency: 'USD' }); </script> -
GA4 implementation
Use the gtag or
dataLayerto send a purchase event withtransaction_id:<script async src="https://www.googletagmanager.com/gtag/js?id=GA_MEASUREMENT_ID"></script> <script> window.dataLayer = window.dataLayer || []; function gtag(){dataLayer.push(arguments)} gtag('js', new Date()); gtag('config', 'GA_MEASUREMENT_ID'); gtag('event', 'purchase', { transaction_id: 'TXN_12345', value: 49.99, currency: 'USD' }); </script>
Best Practices
Guidelines to ensure effective use of Transaction IDs across analytics setups.
-
Consistent formatting
Use a stable schema (e.g.,
TXN_#######) and avoid regenerating IDs on retries. -
Privacy considerations
Do not embed any personal data in the Transaction ID to remain GDPR and CCPA compliant.
-
Event sequencing
Send the ID only after an order is confirmed to prevent tracking abandoned checkouts as purchases.
Common Pitfalls and Troubleshooting
Covers typical errors when implementing Transaction IDs and how to avoid them.
-
Missing id field
Omitting
transaction_idleads to aggregated stats with no order-level granularity. -
Non-unique ids
Reusing IDs across orders causes data collisions and inaccurate metrics.
-
Inconsistent naming
Using different parameter names (e.g.,
order_idvs.transaction_id) breaks integration with analytics APIs.