Published on 2025-06-28T08:49:46Z
What is User Identification? Examples and Use Cases
User Identification is the process of distinguishing individual users within an
analytics system to track their interactions across sessions, devices, and touchpoints. By assigning
unique identifiers—such as cookies, a logged-in user ID, or device fingerprints—analytics platforms can
accurately measure unique users, build customer journey maps, and deliver personalized experiences.
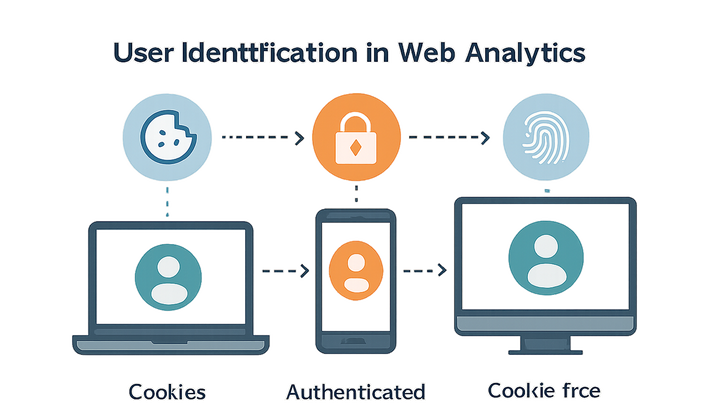
Traditional solutions like GA4 use client_id cookies combined with optional
user_id for authenticated users, while privacy-forward tools like PlainSignal employ
cookie-free techniques to respect user consent and comply with regulations. Effective user identification
balances robust data collection with privacy compliance, ensuring reliable insights in a cookieless
future.
User identification
Tracking individual users across sessions and devices using cookies, user IDs, and cookie-free methods like PlainSignal.
Why User Identification Matters
Understanding who your users are and tracking their behavior over time is foundational to meaningful analytics. Without accurate user identification, metrics like unique user counts, engagement rates, and conversion paths become unreliable, leading to poor decisions. Proper identification underpins segmentation, personalization, retention strategies, and ROI measurement.
-
Accurate audience measurement
Ensures unique visits are properly counted and reduces inflated or duplicated user counts.
-
Data integrity
Recognizes returning users across sessions to avoid treating them as new visitors.
-
Campaign attribution
Accurately credits marketing channels and touchpoints for conversions.
-
-
Customer journey analysis
Links user actions across multiple sessions and devices to visualize the end-to-end experience.
-
Touchpoint consolidation
Stitches interactions from different channels into a coherent path.
-
Funnel optimization
Identifies drop-off points in multi-step processes for targeted improvements.
-
Methods of User Identification
Analytics platforms employ various techniques to assign and persist user identifiers. Each method balances accuracy, implementation complexity, and privacy considerations.
-
Cookie-based identification
Uses browser cookies (e.g., GA4’s
client_id) to assign a persistent identifier. It’s simple but vulnerable to cookie deletion and blocking. -
User authentication (login-based)
Assigns a
user_idwhen users authenticate. It provides high accuracy but only tracks logged-in users. -
Device fingerprinting
Creates a unique signature from device attributes (e.g., browser, OS, screen size). It works without cookies but raises privacy concerns.
-
Cookie-free tracking
Leverages techniques like hashing and local device storage to identify users without cookies. PlainSignal exemplifies this approach.
Implementing User Identification in Analytics Tools
Practical examples of how leading platforms configure user identification, including code snippets.
-
GA4 implementation
GA4 uses
client_idcookies by default and allows setting a customuser_idfor logged-in users.Example of setting
user_idin GA4:gtag('config', 'G-XXXXXXX', { 'user_id': 'USER_ID' }); -
PlainSignal implementation
PlainSignal offers cookie-free user identification via a lightweight script. Add this to your site’s
<head>:<link rel="preconnect" href="//eu.plainsignal.com/" crossorigin /> <script defer data-do="yourwebsitedomain.com" data-id="0GQV1xmtzQQ" data-api="//eu.plainsignal.com" src="//cdn.plainsignal.com/plainsignal-min.js"></script>
Privacy and Compliance
User identification techniques must adhere to data protection regulations and respect user preferences. Implement strategies that balance analytics needs with privacy.
-
Gdpr and cookie consent
Under GDPR, tracking cookies require explicit user consent. Cookie-free solutions reduce the reliance on consent but still need transparent data usage policies.
-
Data minimization & retention
Store only necessary identifiers and define retention periods to mitigate privacy risks and comply with regional laws.