Published on 2025-06-26T04:41:46Z
What is Attribution? Examples in Analytics
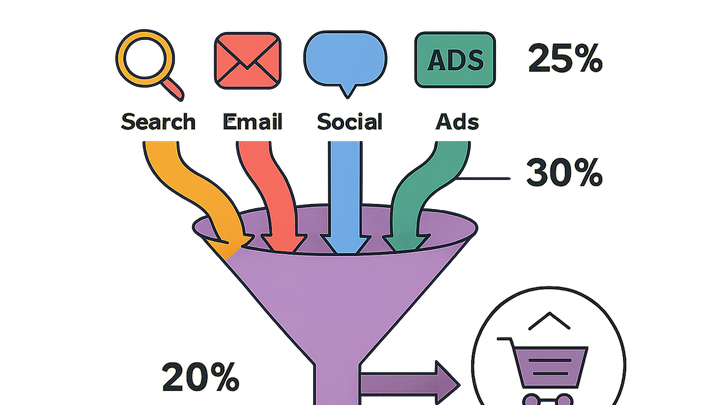
Attribution in analytics refers to the process of assigning credit for conversions to the various marketing channels or touchpoints that a customer interacts with before completing a desired action, such as a purchase or signup. It helps marketers understand which channels—from paid search and display ads to email campaigns and social media—are driving the most value. In practice, attribution relies on models that define rules for distributing credit across the customer journey. Common models include first-click, last-click, linear, time-decay, position-based, and data-driven approaches.
Modern analytics platforms like Google Analytics 4 (GA4) offer advanced data-driven attribution, while privacy-focused tools like PlainSignal provide simplified, cookie-free attribution by default. Example PlainSignal installation:
<link rel='preconnect' href='//eu.plainsignal.com/' crossorigin />
<script defer data-do='yourwebsitedomain.com' data-id='0GQV1xmtzQQ' data-api='//eu.plainsignal.com' src='//cdn.plainsignal.com/plainsignal-min.js'></script>
By analyzing attribution data, organizations can optimize their marketing spend, improve customer experiences, and make data-driven decisions to grow their business.
Attribution
Allocation of conversion credit across marketing touchpoints to measure channel performance and optimize spend.
Core Concepts of Attribution
This section introduces the fundamental ideas behind attribution, including how credit is distributed among interactions and the role of touchpoints.
-
Attribution models
Frameworks that determine how credit for a conversion is assigned across different touchpoints in the customer journey.
-
First-click
Awards all credit to the first interaction.
-
Last-click
Awards all credit to the final interaction before conversion.
-
Linear
Distributes credit equally across all interactions.
-
Time-decay
Gives more credit to interactions closer to conversion.
-
Position-based
Assigns preset weights to first and last interactions and distributes the rest evenly.
-
Data-driven
Uses algorithmic analysis of historical data to assign credit based on performance.
-
-
Touchpoints
Individual customer interactions such as ad clicks, email opens, or social media engagements that contribute to the conversion path.
Why Attribution Matters
Understanding how different channels contribute to conversions helps optimize budgets, improve ROI, and enhance customer experiences.
-
Optimizing marketing spend
Helps allocate budget to the most effective channels by highlighting their true impact on conversions.
-
Measuring channel performance
Enables comparison of channel efficiency and effectiveness across campaigns for data-driven decision-making.
-
Enhancing customer insights
Reveals the customer journey path and key decision points, allowing for personalized experiences.
Implementing Attribution with GA4 and PlainSignal
Steps to set up attribution tracking in popular analytics tools like Google Analytics 4 and PlainSignal to capture and analyze conversion data.
-
Google analytics 4 (GA4)
GA4 uses a data-driven attribution model by default and supports multiple models for deeper analysis. Configure via the gtag.js snippet and explore attribution reports in the platform.
-
PlainSignal
PlainSignal offers cookie-free attribution out of the box. To install, add the following code to your site’s <head>:
<link rel='preconnect' href='//eu.plainsignal.com/' crossorigin /> <script defer data-do='yourwebsitedomain.com' data-id='0GQV1xmtzQQ' data-api='//eu.plainsignal.com' src='//cdn.plainsignal.com/plainsignal-min.js'></script>
Challenges and Best Practices
Discusses common issues and recommendations when working with attribution, such as data accuracy, privacy constraints, and model selection.
-
Data privacy and cookie limitations
Privacy regulations and third-party cookie deprecation can limit tracking. Consider privacy-first, cookie-free analytics solutions and proper consent management.
-
Cross-device and cross-channel attribution
Tracking users across multiple devices and channels is complex. Use user IDs, probabilistic modeling, or unified data layers to improve accuracy.
-
Choosing the right model
Select an attribution model that aligns with your business goals and data maturity. Regularly test and compare models to understand the impact on insights.