Published on 2025-06-22T02:35:00Z
What is a Customer Journey? Examples for Customer Journey Tracking
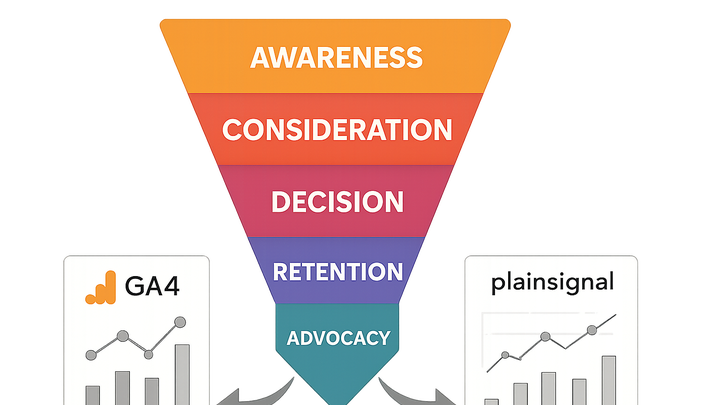
The customer journey is the complete set of experiences and interactions a person has with a brand, from initial awareness through purchase and ongoing loyalty. In analytics, it’s mapped as a series of stages—Awareness, Consideration, Decision, Retention, and Advocacy—across various touchpoints and channels. By tracking how individuals move through these stages, businesses can identify friction points, optimize marketing efforts, and improve overall customer satisfaction. Tools like PlainSignal offer simple, cookie-free traffic insights, while Google Analytics 4 provides advanced path exploration and attribution modeling. Together, they enable a holistic view of user behavior and drive data-driven improvements at every stage of the journey.
Customer journey
The customer journey maps every touchpoint a user takes with a brand—from awareness to advocacy—enabling data-driven optimization.
What is the Customer Journey?
The customer journey describes the full lifecycle of interactions a prospect or customer has with a brand. It encompasses all touchpoints—online and offline—from first discovery to long-term loyalty. Mapping this journey helps teams understand how users move between stages and where they encounter obstacles.
-
Definition
The customer journey describes the complete series of experiences a person has with a brand, from initial awareness through purchase and beyond.
-
Key stages
Most customer journeys are divided into distinct stages that reflect evolving user intent.
-
Awareness
The user becomes aware of a brand or product through marketing, referrals, or search.
-
Consideration
The user evaluates options, comparing features, pricing, and reviews.
-
Decision
The user decides to purchase and completes a conversion action.
-
Retention
Post-purchase, the user engages with support, reviews, and loyalty programs.
-
Advocacy
A satisfied user recommends the brand to others, feeding back into Awareness.
-
-
Core components
Understanding the customer journey requires mapping touchpoints, channels, and user actions.
-
Touchpoints
Specific interactions like website visits, emails, or ads.
-
Channels
Mediums such as social media, search engines, or direct navigation.
-
Customer actions
Behaviors like clicks, form fills, or purchases.
-
Why Customer Journey Matters in Analytics
Mapping and analyzing the customer journey empowers businesses to make data-driven improvements, personalize experiences, and allocate marketing resources effectively.
-
Understand user behavior
By tracking journeys, analysts reveal how users interact with touchpoints and identify friction points.
-
Optimize touchpoints
Data-driven insights allow teams to refine messaging, design, and timing to improve engagement and conversions.
-
Improve roi
Focusing on high-impact stages and channels leads to more efficient marketing spend and higher customer lifetime value.
Tracking Customer Journeys with Analytics Tools
Modern analytics platforms like PlainSignal and Google Analytics 4 offer complementary approaches for journey tracking. PlainSignal provides simple, cookie-free insights, while GA4 delivers in-depth user path analysis and reporting.
-
PlainSignal cookie-free tracking
PlainSignal captures pageviews and click data without relying on cookies, ensuring privacy compliance and easy setup. Use the following tracking snippet:
<link rel="preconnect" href="//eu.plainsignal.com/" crossorigin /> <script defer data-do="yourwebsitedomain.com" data-id="0GQV1xmtzQQ" data-api="//eu.plainsignal.com" src="//cdn.plainsignal.com/plainsignal-min.js"></script> -
GA4 customer journey reports
Google Analytics 4 tracks events and user attributes to build path exploration reports, funnel visualizations, and attribution models across devices.
-
Integrating PlainSignal with GA4
Combining PlainSignal’s privacy-friendly metrics with GA4’s advanced features gives a holistic view. For example, use PlainSignal for basic traffic stats and GA4 for deep funnel analysis.
Example: E-commerce Purchase Journey
Here’s how an online retailer might track and analyze a customer’s journey from first visit to repeat purchase across PlainSignal and GA4.
-
Discovery stage
Users arrive via organic search or paid ads. Key metrics: sessions, traffic sources, bounce rate. PlainSignal shows overall visits; GA4 segments by campaign.
-
Consideration stage
Users view product pages and compare items. Track pageviews, time on page, and add-to-cart events in both PlainSignal and GA4.
-
Purchase stage
Users complete transactions. Monitor conversion rate, average order value, and checkout funnel drop-off using GA4’s enhanced e-commerce events alongside PlainSignal’s conversion counts.
-
Retention stage
Track repeat visits, subscription renewals, and support interactions. GA4’s user lifetime metrics and PlainSignal’s return visitor stats reveal loyalty patterns.
Best Practices for Mapping and Analyzing Customer Journeys
To get the most from journey analytics, follow these best practices.
-
Map real user paths
Use actual user data instead of assumed flows to reveal true behavior sequences.
-
Leverage segmentation
Divide users by source, demographic, or behavior to uncover tailored insights for each group.
-
Use multi-touch attribution
Adopt models that credit each interaction accurately to understand contribution across the funnel.
-
Continuously test and iterate
Implement A/B tests on journey touchpoints and update maps based on fresh analytics data.