Published on 2025-06-28T04:19:19Z
What is a Channel in Analytics? Examples with Google Analytics 4 and PlainSignal
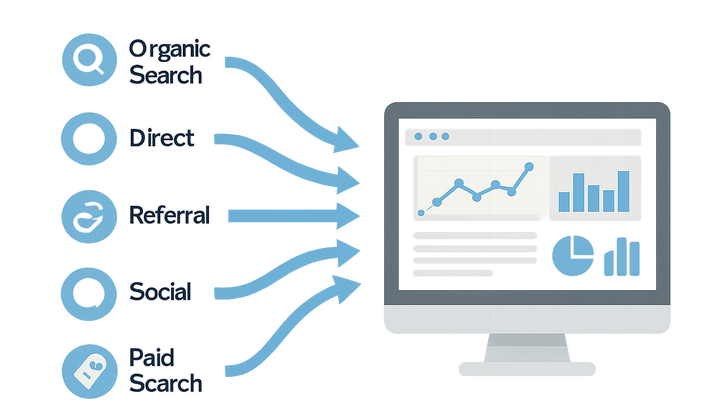
In analytics, a Channel refers to a high-level grouping of traffic sources through which users arrive at your website or app, such as Organic Search, Direct, Referral, Social, Paid Search, and Email Marketing. By organizing visits into channels, marketers and analysts can simplify data segmentation, compare performance across key traffic categories, and make informed decisions about budget allocation and campaign optimization. Platforms like Google Analytics 4 provide default channel definitions and leverage gtag.js with UTM parameters to attribute traffic, whereas privacy-focused tools like PlainSignal offer cookie-free tracking using lightweight scripts and referrer-based logic. Accurate channel attribution is essential for measuring marketing ROI, understanding user acquisition paths, and conducting cross-channel analyses. Misclassification or inconsistent tagging can lead to skewed insights and missed opportunities, highlighting the importance of standardized UTM conventions, regular data audits, and aligning channel settings with business objectives.
Channel
Channels group visitor traffic by source (e.g., Organic Search, Direct, Paid), enabling marketers to compare performance and optimize marketing efforts.
What is a Channel in Analytics?
An overview of the core concept and importance of channels in web analytics.
-
Definition
A channel is a categorized grouping of traffic sources through which users find and access your website or app, such as search engines, direct visits, referrals, or paid ads.
-
Purpose
Channels simplify traffic segmentation, allowing analysts to quickly assess and compare how different types of sources contribute to goals like conversions or engagement.
Common Channel Groupings
Default channel categories used by analytics platforms like GA4 and PlainSignal.
-
Organic search
Visitors arriving through unpaid search engine results.
-
Direct
Users who enter your URL directly or via bookmarks without a referring source.
-
Referral
Traffic coming from links on other websites, excluding search engines and social networks.
-
Social
Visits originating from social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, or LinkedIn.
-
Paid search
Users clicking on paid advertising campaigns in search engine results.
-
Email marketing
Visitors who arrive via links in email campaigns.
How Channels are Tracked
Methods used by analytics tools to attribute traffic to channels.
-
Google analytics 4
GA4 uses the gtag.js library and UTM parameters to automatically classify channels based on URL tags and referrer data.
-
Gtag.js initialization
Load the gtag.js snippet or configure via Google Tag Manager to start tracking pageviews and events.
-
Utm parameters
Append UTM source, medium, and campaign tags to URLs to override default channel attribution for campaign-level tracking.
-
-
PlainSignal
A lightweight, cookie-free analytics tool that infers channels using a simple script and referrer-based logic.
-
Preconnect and script tags
Include the following HTML snippet to enable PlainSignal tracking on your site:
-
Example code
<link rel="preconnect" href="//eu.plainsignal.com/" crossorigin /> <script defer data-do="yourwebsitedomain.com" data-id="0GQV1xmtzQQ" data-api="//eu.plainsignal.com" src="//cdn.plainsignal.com/plainsignal-min.js"></script>
-
Importance of Accurate Channel Attribution
Why proper channel grouping and attribution is vital for business insights and ROI measurement.
-
Marketing roi
Accurate channel data allows teams to measure the return on investment for each marketing channel and optimize budget allocation.
-
Campaign optimization
Identifying top-performing channels helps refine targeting strategies and creative decisions.
-
Holistic insights
Comprehensive channel data supports cross-channel analysis and informs end-to-end customer journey mapping.
Best Practices
Recommendations to maintain clean, reliable channel data.
-
Standardize utm usage
Define and enforce consistent UTM parameter conventions across teams and campaigns.
-
Review channel settings
Check default channel definitions in your analytics tool and adjust as needed to match your business logic.
-
Regular data audits
Periodically audit channel reports to identify and correct misclassifications or missing attribution.
-
Consider privacy and compliance
Use privacy-friendly tracking methods like PlainSignal or server-side tagging to maintain data accuracy without cookies.