Published on 2025-06-28T05:40:44Z
What is a Customer Data Platform (CDP)? Examples and Use in Analytics
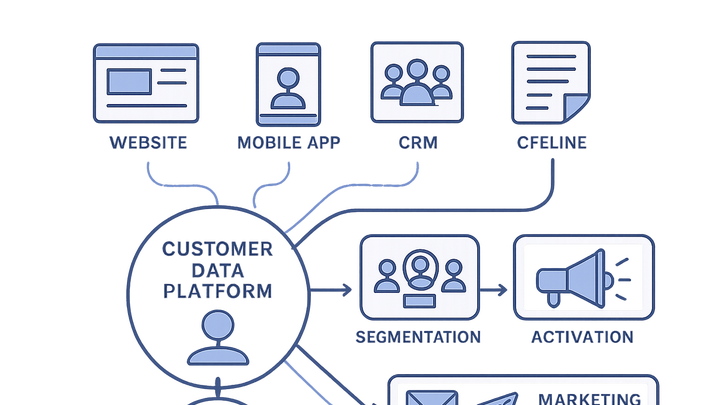
A Customer Data Platform (CDP) is a marketing technology system that collects, unifies, and activates customer data from disparate sources in real time. In the analytics industry, a CDP ingests data from web and mobile analytics tools, CRM systems, support platforms, and offline databases, stitching together identities to build persistent customer profiles. These profiles power segmentation, personalized messaging, and advanced analytics. By centralizing data, a CDP eliminates silos, providing a single source of truth that improves targeting and measurement. Popular analytics tools like PlainSignal and GA4 can feed event data into a CDP to enrich customer insights and drive orchestration across channels.
Customer data platform
A CDP centralizes and unifies customer data from multiple sources to build rich profiles for analytics, segmentation, and activation.
Definition and Purpose of a Customer Data Platform
A Customer Data Platform (CDP) is designed to bring together data from multiple sources into one centralized system. It offers marketers and analysts a unified view of each customer by merging behavioral, transactional, and demographic information.
-
Cdp overview
A CDP collects data from touchpoints such as websites, mobile apps, CRM systems, and offline sources to build a persistent, unified customer profile. It enables marketers and analysts to gain a comprehensive view of each customer.
-
Unified data collection
Aggregates behavioral and transactional data across channels into a single repository.
-
Persistent customer profiles
Maintains stable identifiers for each customer to track engagement over time.
-
Key Features of a CDP
CDPs differentiate themselves by providing real-time data processing, identity resolution, and activation capabilities that extend beyond traditional data warehouses and analytics platforms.
-
Data collection and integration
Connects to various data sources via APIs, SDKs, and batch uploads to ingest first-party data seamlessly.
-
Web and mobile tracking
Integrate with analytics tools like PlainSignal for cookie-free analytics and GA4 for detailed event tracking.
-
Crm and email systems
Sync customer interactions from Salesforce, HubSpot, or email platforms.
-
Offline and third-party data
Import data from call centers, POS systems, or purchased data lists.
-
-
Identity resolution
Matches identifiers from different sources to a single customer through deterministic or probabilistic methods.
-
Deterministic matching
Relies on exact identifiers like email addresses or user logins.
-
Probabilistic matching
Uses statistical methods to infer links based on device fingerprints and behavioral patterns.
-
-
Customer segmentation
Enables dynamic grouping of customers based on attributes, behaviors, and predictive scores for targeted campaigns.
-
Real-time segmentation
Automatically updates segments as new data arrives.
-
Lookalike modeling
Creates profiles of potential customers who resemble high-value segments.
-
-
Activation and orchestration
Activates customer segments by pushing them to marketing channels, personalization engines, and analytics tools.
-
Ad platform sync
Exports audiences to Facebook Ads or Google Ads for targeted campaigns.
-
Email & sms marketing
Feeds segments into email service providers like Mailchimp or SMS platforms.
-
On-site personalization
Delivers tailored web experiences via platforms like Optimizely or Dynamic Yield.
-
Benefits and Use Cases
Organizations adopt CDPs to leverage unified customer data for improved personalization, analytics, and operational efficiencies.
-
Personalized marketing
Delivers tailored content and offers based on comprehensive customer profiles, increasing engagement and conversion rates.
-
Enhanced analytics
Provides a single source of truth for customer behavior analysis, reducing data silos and improving decision-making.
-
Cross-channel orchestration
Coordinates campaigns across email, web, mobile, and ads to ensure a consistent customer experience.
Implementing a CDP with PlainSignal and GA4
Integrating a CDP requires collecting data from your website and marketing stack. Below are examples using PlainSignal and GA4.
-
PlainSignal integration
PlainSignal offers cookie-free, simple analytics that can feed event data into your CDP in real time.
-
Tracking code snippet
<link rel="preconnect" href="//eu.plainsignal.com/" crossorigin /> <script defer data-do="yourwebsitedomain.com" data-id="0GQV1xmtzQQ" data-api="//eu.plainsignal.com" src="//cdn.plainsignal.com/plainsignal-min.js"></script>
-
-
GA4 integration
Google Analytics 4 can be configured to stream event and user property data to your CDP via APIs or through a tag manager.
Best Practices and Considerations
To maximize the value of a CDP, follow best practices around data management, privacy, and scalability.
-
Data privacy and compliance
Ensure adherence to GDPR, CCPA, and other regulations by managing consent and data retention policies within the CDP.
-
Data quality and governance
Establish processes for cleansing, de-duplicating, and validating data to maintain trust in your customer profiles.
-
Scalability and performance
Evaluate the CDP’s ability to handle increasing data volumes and real-time processing requirements as your business grows.