Published on 2025-06-27T19:24:57Z
What is Marketing ROI? Examples and Calculation
Marketing ROI, or Return on Investment, measures how much revenue is generated by marketing activities relative to their costs. It’s a critical metric in analytics that helps marketers determine which channels and campaigns yield the highest returns on spend. By calculating marketing ROI, organizations can optimize budgets, forecast future performance, and demonstrate the tangible value of marketing investments to stakeholders. Modern analytics platforms like Google Analytics 4 (GA4) and cookie-free solutions like PlainSignal enable detailed ROI tracking by capturing revenue data alongside marketing costs. This glossary entry explores the definition, calculation formula, practical examples, and best practices for Marketing ROI.
Marketing roi
Metric showing revenue return from marketing spend, guiding budget allocation and campaign performance.
Why Marketing ROI Matters
Marketing ROI provides a clear benchmark for evaluating the effectiveness of marketing spend. It helps businesses allocate budgets to the highest-performing channels, justify marketing investments to stakeholders, and set realistic performance goals. Tracking ROI ensures continuous optimization and maximizes return on every dollar spent.
-
Budget optimization
ROI data highlights which channels deliver the best returns, enabling marketers to reallocate spend away from underperforming tactics.
-
Performance measurement
By comparing returns to costs, ROI reveals the true effectiveness of campaigns beyond surface-level metrics like clicks or impressions.
-
Stakeholder communication
A clear ROI metric translates marketing results into financial terms, making it easier to communicate value to executives and investors.
How to Calculate Marketing ROI
Calculating Marketing ROI involves identifying total campaign costs and attributing the correct amount of revenue. The basic formula and considerations such as attribution windows and incremental value play a key role in accurate measurement.
-
Basic roi formula
Use the formula: (Revenue – Cost) / Cost × 100% to express ROI as a percentage.
-
Revenue
Total sales or income directly generated by a specific marketing campaign.
-
Cost
All expenses associated with the campaign, including ad spend, tools, and agency fees.
-
-
Attribution window
The time period over which conversions are credited to a campaign affects the revenue figure in the ROI formula.
-
Short window
Typically 24–48 hours post-click, useful for direct response campaigns.
-
Long window
Up to 90 days or more, capturing delayed conversions common in B2B or high-consideration purchases.
-
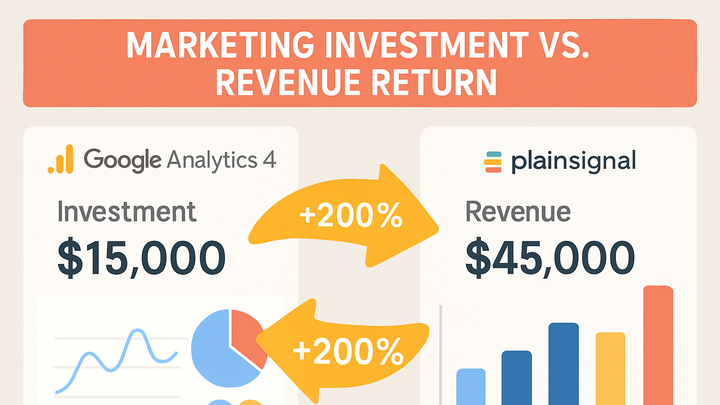
Examples in GA4 and PlainSignal
Different analytics platforms offer built-in and customizable methods for tracking marketing ROI. Below are practical examples using GA4 and the cookie-free analytics tool PlainSignal.
-
Tracking roi in google analytics 4
In GA4, import cost data from Google Ads or third-party channels, configure revenue events, and use the ROI metric in custom reports or dashboards.
-
Cookie-free roi with PlainSignal
PlainSignal provides simple tracking of sessions and revenue without cookies, making it GDPR and CCPA compliant while still enabling ROI calculations.
-
Sample tracking code
Implement PlainSignal’s tracking snippet on your site to start capturing data:
-
Code snippet
<link rel="preconnect" href="//eu.plainsignal.com/" crossorigin /> <script defer data-do="yourwebsitedomain.com" data-id="0GQV1xmtzQQ" data-api="//eu.plainsignal.com" src="//cdn.plainsignal.com/plainsignal-min.js"></script>
-
Best Practices and Considerations
Adhering to best practices ensures your Marketing ROI calculations are accurate, repeatable, and actionable across different campaigns and channels.
-
Include all relevant costs
Factor in indirect costs such as creative development, software subscriptions, and personnel time to avoid overstated ROI.
-
Standardize attribution models
Use consistent attribution rules across campaigns to enable fair comparisons and trend analysis.
-
Combine with other metrics
Analyze ROI alongside metrics like CAC and LTV for a more comprehensive understanding of marketing impact.
-
Periodically re-evaluate
Regularly recalculate ROI to account for market shifts, seasonality, and evolving campaign objectives.