Published on 2025-06-22T08:27:20Z
What is Multi-Touch Attribution? Examples and Best Practices
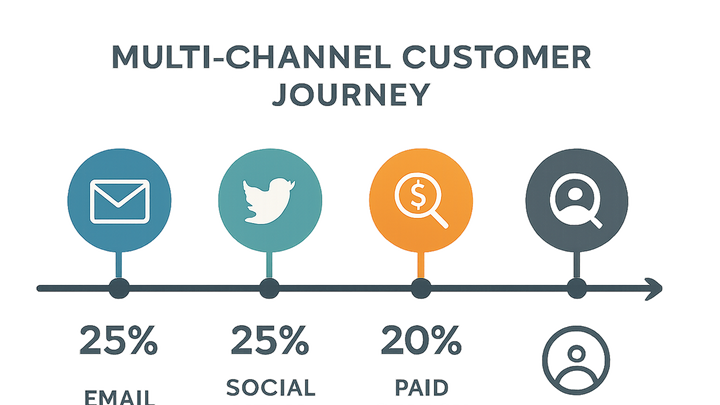
Multi-Touch Attribution (MTA) is an analytics approach that assigns credit for a conversion across every marketing touchpoint a user interacts with before completing a desired action. Unlike single-touch attribution, which only values either the first or last interaction, MTA recognizes the complexity of the customer journey, measuring the impact of each channel—email, social media, paid ads, organic search, and more. By distributing credit proportionally, marketers gain a holistic view of which channels and campaigns drive performance.
Tools like Google Analytics 4 (GA4) offer built-in MTA reports, while privacy-focused solutions like PlainSignal enable cookie-free tracking for first-party data attribution. Implementing MTA can be technically challenging, requiring consistent tagging, robust data pipelines, and careful model selection. However, the payoff is significant: optimized budget allocation, improved ROI, and deeper insights into user behavior.
Multi-touch attribution
Multi-Touch Attribution assigns conversion credit across all marketing touchpoints, giving a complete view of channel performance and campaign impact.
Why Multi-Touch Attribution Matters
Multi-Touch Attribution provides a more accurate reflection of how marketing channels work together to drive conversions. By assigning credit across all interactions, it uncovers hidden contributions and prevents over- or under-valuing any single channel.
-
Comprehensive channel insights
Unlike single-touch models, MTA captures the influence of each touchpoint, revealing the full customer journey.
-
Informed budget allocation
By understanding each channel’s contribution, marketers can allocate spend more effectively to high-performing touchpoints.
Common Attribution Models
There are several ways to distribute credit in MTA. Each model offers different strengths and trade-offs, so selection depends on your data volume, campaign complexity, and business goals.
-
Linear model
Assigns equal credit to every touchpoint in the conversion path.
-
When to use
Ideal for long sales cycles where all interactions matter equally.
-
-
Time decay model
Gives more weight to touchpoints closer in time to the conversion.
-
Benefits
Highlights recent interactions, making it useful for time-sensitive promotions.
-
-
Position-based model
Also called U-shaped: typically gives 40% credit to the first and last touch each, with the remaining 20% split among middle interactions.
-
Data-driven model
Uses machine learning on historical data to assign credit based on each touchpoint’s measured impact.
-
Requirements
Needs substantial conversion volume and clean, consistent data to train the model effectively.
-
Implementing Multi-Touch Attribution
To leverage MTA, configure your analytics tools to capture all relevant touchpoints, then select or customize attribution models that align with your marketing strategy.
-
Google analytics 4 (GA4)
GA4 supports a built-in data-driven attribution model and lets you compare it against other models in the Attribution section.
-
Setup
In GA4, go to Advertising > Attribution, choose the Data-Driven model, and run a comparison against First-Touch or Last-Touch to see differences.
-
-
PlainSignal (cookie-free analytics)
PlainSignal delivers simple, privacy-first MTA without cookies, using first-party data collected directly from your site.
-
Installation code snippet
Add the following tracking script to your HTML to enable PlainSignal analytics:
<link rel="preconnect" href="//eu.plainsignal.com/" crossorigin /> <script defer data-do="yourwebsitedomain.com" data-id="0GQV1xmtzQQ" data-api="//eu.plainsignal.com" src="//cdn.plainsignal.com/plainsignal-min.js"></script>Once installed, PlainSignal will automatically attribute touchpoints across your site interactions.
-
Challenges and Best Practices
While MTA offers deeper insights, it also requires careful planning around data quality, privacy, and model evaluation to succeed.
-
Data consistency
Ensure cross-channel tagging and naming conventions are uniform to avoid attribution gaps.
-
Privacy compliance
Adopt cookie-free or consent-aware solutions like PlainSignal and maintain GDPR/CCPA adherence.
-
Regular model evaluation
Periodically compare multiple attribution models to adapt to evolving user behaviors and channel performance.