Published on 2025-06-28T08:25:30Z
What is a Referral Code? Examples and Tracking
A referral code is a unique identifier appended to a promotional URL to attribute user sign-ups,
conversions, or other key actions to specific referrers such as affiliates, influencers, or existing
customers. In analytics, referral codes help marketing teams measure which channels or individuals drive
the most valuable traffic. Each code typically appears as a query parameter (for example,
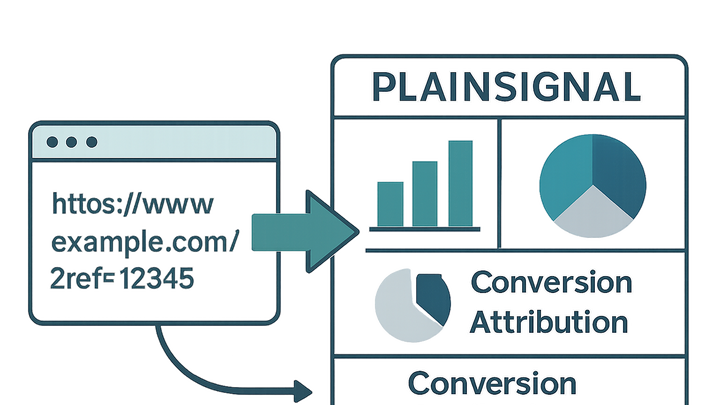
?ref=SUMMER2025) and can be captured by modern analytics platforms. PlainSignal, a
cookie-free analytics solution, automatically records defined query parameters including referral codes
without requiring additional setup beyond installing its script. In Google Analytics 4 (GA4), you can
track referral codes by creating a custom dimension or user property and sending the code value as part of
your page_view or custom events. Properly implemented, referral code tracking empowers teams
to optimize referral programs, calculate return on investment, and understand user acquisition strategies
in depth.
Referral code
A referral code is a unique identifier used in analytics to attribute conversions or sign-ups to specific referrers via tracked links.
Definition and Purpose
This section explains what a referral code is and why it’s used in analytics.
-
Referral code basics
A referral code is a short alphanumeric string added as a query parameter (often
ref) to a URL. When a new user arrives via that link, the code tells your analytics platform who or what campaign referred them.-
Structure
Typically a few characters long (e.g.,
REF123,SUMMER2025), easy to share and track. -
Use cases
Common in affiliate programs, influencer marketing, word-of-mouth campaigns, and customer referral incentives.
-
Importance in Analytics
Referral codes are critical for accurate attribution and performance measurement across marketing channels.
-
Conversion attribution
They allow you to assign credit for sign-ups, purchases, or other goals directly to the referrer or campaign.
-
Performance measurement
By comparing referral code usage, you can calculate ROI, optimize incentive structures, and identify high-value partners.
Implementing Referral Code Tracking with SaaS Platforms
Step-by-step instructions for capturing referral codes in PlainSignal and GA4.
-
PlainSignal (cookie-free analytics)
Add the PlainSignal script to your site head, and it will automatically record any predefined query parameters like
ref.<link rel="preconnect" href="//eu.plainsignal.com/" crossorigin /> <script defer data-do="yourwebsitedomain.com" data-id="0GQV1xmtzQQ" data-api="//eu.plainsignal.com" src="//cdn.plainsignal.com/plainsignal-min.js"></script>-
Integration
Paste the provided script snippet into your
<head>so PlainSignal can load before page views. -
Parameter capture
In the PlainSignal dashboard, define
ref(or your custom key) as a tracked URL parameter.
-
-
Google analytics 4 (GA4)
Configure GA4 to capture the
refparameter via a custom dimension or event.<script async src="https://www.googletagmanager.com/gtag/js?id=G-XXXXXXX"></script> <script> window.dataLayer = window.dataLayer || []; function gtag(){dataLayer.push(arguments);} gtag('js', new Date()); // Map the 'ref' URL parameter to a custom dimension gtag('config', 'G-XXXXXXX', { 'custom_map': { 'dimension1': 'referral_code' } }); // Send referral_code in page_view event gtag('event', 'page_view', { 'referral_code': getParameterByName('ref') }); </script>-
Set up custom dimension
In the GA4 admin UI, create a user-scoped or event-scoped custom dimension named
referral_code. -
Event configuration
Use
gtag('event', 'page_view', {...})to send thereferral_codevalue on each page load.
-
Best Practices and Considerations
Guidelines to ensure your referral code strategy is effective, secure, and privacy-compliant.
-
Naming conventions
Use concise, human-readable codes and keep formats consistent across campaigns.
-
Privacy compliance
Avoid including personal data in codes. Ensure you have user consent before tracking.
-
Data validation
Implement server- or client-side checks to filter out invalid or spammy codes.