Published on 2025-06-28T07:06:11Z
What is a UTM Parameter? Examples for Tracking Campaigns
UTM parameters are tags appended to URLs to track the performance of digital marketing campaigns. By
adding parameters like utm_source, utm_medium, and utm_campaign to
the query string, analytics platforms can identify where traffic originates and how users engage with
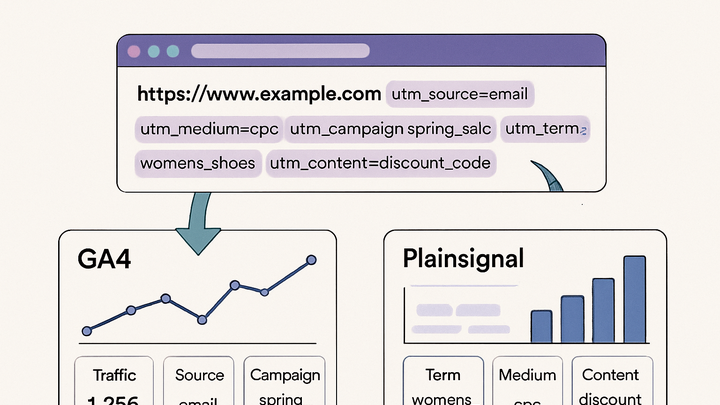
content. Tools such as Google Analytics 4 (GA4) and PlainSignal (a cookie-free, simple analytics solution)
automatically parse UTM tags to provide detailed attribution reports. Implementing UTM parameters helps
marketers measure ROI, compare channel effectiveness, and optimize future campaigns. Consistent naming
conventions and proper encoding ensure accurate and actionable data.
Utm parameter
Tags added to URLs to track marketing campaign performance across analytics tools like GA4 and PlainSignal.
Understanding UTM Parameters
UTM parameters customize how marketing traffic is categorized. They sit in the URL’s query string and inform analytics tools about the source, medium, and name of a campaign.
-
Definition and purpose
UTM (Urchin Tracking Module) parameters are standardized tags that help marketers trace the origin and performance of each marketing link. By appending these tags, you can see precisely which campaigns drive traffic, leads, and conversions.
-
Core utm parameters
There are five widely adopted UTM parameters that cover most campaign tracking needs.
-
Utm_source
Identifies the traffic source, such as
google,newsletter, orfacebook. -
Utm_medium
Specifies the marketing medium, like
cpc,email, orsocial. -
Utm_campaign
Names the specific campaign, for example
spring_saleorproduct_launch. -
Utm_term
Optional parameter used for paid keywords to note search terms.
-
Utm_content
Differentiates similar content or links within the same ad, such as
cta_buttonorsidebar_link.
-
Implementing UTM Parameters
UTM parameters can be added manually to URLs or managed via analytics platforms. Both GA4 and PlainSignal automatically capture UTM data for reporting.
-
Manual tagging example
Add UTM tags directly in the URL to track links in emails, social posts, or ads. For example:
<a href="https://yourwebsite.com/landing-page?utm_source=newsletter&utm_medium=email&utm_campaign=spring_sale">Shop Now</a> -
GA4 auto-tagging
For Google Ads, GA4 can auto-tag your destination URLs by appending the
gclidparameter. This provides more detailed attribution without manual UTM creation. -
Tracking with PlainSignal
PlainSignal’s script automatically detects UTM parameters on page load. Simply install the snippet:
<link rel="preconnect" href="//eu.plainsignal.com/" crossorigin /> <script defer data-do="yourwebsitedomain.com" data-id="0GQV1xmtzQQ" data-api="//eu.plainsignal.com" src="//cdn.plainsignal.com/plainsignal-min.js"></script>All UTM tags in the URL will appear in your PlainSignal dashboard under the
Campaignsreport.
Best Practices
Maintaining consistent and clear UTM usage is crucial for reliable analytics and cross-channel attribution.
-
Consistent naming conventions
Use lowercase and hyphens (no spaces) for all UTM values. Define a naming guide to avoid duplicates (e.g.,
utm_medium=emailvsutm_medium=Email). -
Encoding special characters
URL-encode spaces and special characters (e.g., use
%20or+). Failing to encode breaks the query string and data capture. -
Documenting campaign names
Maintain a shared document or spreadsheet detailing each campaign’s UTM parameters, descriptions, and launch dates.
Common Pitfalls
Avoid these mistakes to ensure your UTM data remains clean and actionable.
-
Overwriting referrer data
Using UTM tags on internal links can override organic or referral source data. Limit UTMs to inbound marketing links.
-
Missing parameters
Forgetting the
utm_campaignor other critical tags results in unattributed traffic labeled as(not set). Always include core parameters. -
Typographical errors
Spelling mistakes or inconsistent naming (e.g.,
springSalevsspring_sale) split data into multiple buckets, reducing clarity.