Published on 2025-06-22T10:09:00Z
What is a User Flow? Examples with GA4 and PlainSignal
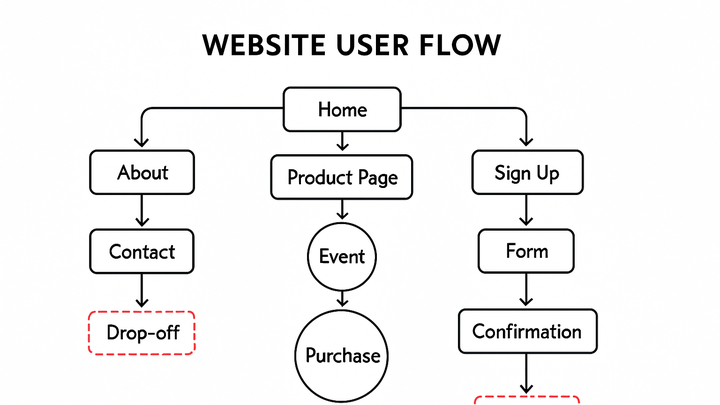
A user flow is a representation of the path that visitors take through a website or application as they complete specific tasks or achieve goals. In analytics, user flows help visualize the sequence of pages and interactions, highlighting how users navigate from entry to conversion or exit points. By analyzing these flows, businesses can identify friction points, optimize navigation, and improve overall user experience. User flows can be tracked and visualized using analytics platforms like Google Analytics 4 (GA4) and cookie-free tools such as PlainSignal. These platforms map each step a user takes – from the landing page through events like clicks, form submissions, and purchases – giving data-driven insights into user behavior. Understanding user flows is critical for enhancing conversion rates, reducing drop-offs, and creating intuitive digital journeys.
User flow
A user flow maps steps users take on a website or app, visualizing navigation and drop-offs to guide UX optimization.
What is a User Flow?
User flows illustrate the journey a visitor takes through your website or app. They trace each step – from landing pages, clicks, and interactions, to final outcomes like form submissions or purchases. By visualizing these paths, you gain a clear picture of how users engage with your content and where they might encounter friction.
-
Definition
A user flow is a sequence of steps or interactions a user performs to achieve a specific goal on a website or application.
-
Components
User flows consist of nodes (pages or screens) and edges (the actions or events connecting them), such as clicks, form submissions, or AJAX calls.
Why User Flows Matter in Analytics
Analyzing user flows helps you understand how visitors move through your site, where they drop off, and which paths lead to conversions. User flows reveal how effectively your site guides visitors toward desired actions. They help uncover usability issues, highlight high-performing navigation paths, and identify drop-off points where users abandon the process. Armed with this insight, teams can prioritize UX improvements and A/B tests to boost engagement and conversions.
-
Optimize navigation
Pinpoint unexpected navigation patterns to simplify menus and CTAs, making it easier for users to find what they need.
-
Improve conversion
Identify stages with high drop-off rates and test changes—like clearer CTAs or streamlined forms—to increase completion rates.
-
Drop-off rate analysis
Measure the percentage of users who exit at each step to find and fix friction points.
-
How to Track User Flows with SaaS Products
Both GA4 and PlainSignal offer features to map and analyze user flows. GA4 provides built-in Funnel and Path Exploration reports, while PlainSignal delivers cookie-free flow tracking with a lightweight snippet. Choosing the right tool depends on your data privacy requirements, ease of setup, and reporting needs.
-
Google analytics 4 (GA4)
In GA4, navigate to Explore > Path Exploration to visualize user journeys. You can set up custom funnels under Analysis to track specific conversion paths. Use segments to isolate behaviors by user dimension or event properties.
-
PlainSignal
PlainSignal offers simple, cookieless analytics with a focus on privacy. Implement the following snippet to start capturing user flows:
<link rel="preconnect" href="//eu.plainsignal.com/" crossorigin /> <script defer data-do="yourwebsitedomain.com" data-id="0GQV1xmtzQQ" data-api="//eu.plainsignal.com" src="//cdn.plainsignal.com/plainsignal-min.js"></script>
Best Practices for User Flow Analysis
Consistent naming conventions, clear goal definitions, and proper segmentation are keys to effective user flow analysis.
-
Define clear goals
Establish specific objectives for each flow, such as ‘complete checkout’ or ‘sign up for newsletter’.
-
Label key events
Use consistent event names (e.g.,
add_to_cart,page_view) to ensure flows remain accurate and comparable. -
Use segmentation
Break down flows by user attributes (location, device, traffic source) to uncover hidden patterns.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Awareness of typical mistakes prevents misleading conclusions and wasted effort.
-
Incomplete event tracking
Missing or misconfigured events can leave gaps in your flows. Verify that all critical interactions are tracked.
-
Ignoring mobile flows
Mobile user behavior often differs from desktop. Analyze flows separately to capture mobile-specific issues.
-
Overlooking context
External factors like marketing campaigns or site changes can skew flow data. Annotate reports with relevant events.