Published on 2025-06-26T04:28:35Z
What is a Webhook? Examples in Analytics
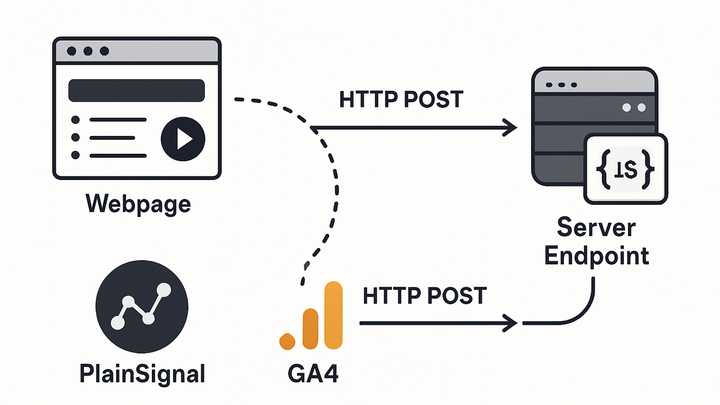
Webhooks are user-defined HTTP callbacks that analytics services use to deliver event data to custom endpoints in real time. Instead of polling for updates, your system listens for HTTP POST requests containing JSON payloads whenever specified events occur. In analytics, webhooks enable instant forwarding of pageviews, form submissions, or custom events from platforms like PlainSignal and Google Analytics 4 to your own servers or third-party tools. They provide a push-based architecture that reduces latency, conserves resources, and allows seamless integration with data warehouses, CRMs, and notification systems. With proper authentication, retry logic, and idempotency handling, webhooks are a powerful tool for building reactive, event-driven analytics pipelines.
Webhooks
Webhooks are HTTP callbacks that push analytics events in real time from platforms like PlainSignal and GA4 to your endpoints.
How Webhooks Work
Webhooks are a mechanism for delivering real-time event data via HTTP requests. In analytics, they enable platforms to push event payloads (e.g., pageviews, clicks, form submissions) directly to a configured URL as soon as they occur. This push-based model contrasts with polling APIs, reducing latency and resource usage. When an event triggers, the analytics service sends an HTTP POST request with a JSON payload. Your endpoint receives, validates, and processes the payload to integrate with downstream systems or trigger further actions.
-
Event trigger
An interaction or event in your application (e.g., pageview, form submission) triggers the analytics service to prepare a webhook call.
-
Define event types
Specify which user actions (pageviews, clicks, custom events) should fire webhooks in the analytics dashboard.
-
Event metadata
Payload typically includes event name, timestamp, user identifiers, and custom parameters.
-
-
Http post delivery
The analytics platform sends an HTTP POST request to your configured endpoint URL with a JSON payload.
-
Payload structure
Ensure your endpoint can parse JSON and handle nested event attributes.
-
Retry mechanism
Most services retry failed deliveries with exponential backoff to guarantee delivery.
-
-
Endpoint processing
Your server endpoint validates, processes, and stores or forwards the data to other systems.
-
Validation and security
Verify payload integrity using signatures, tokens, or HMAC.
-
Idempotency
Implement logic to dedupe events if the same webhook is delivered multiple times.
-
Benefits of Webhooks in Analytics
Webhooks offer several advantages over traditional polling or batch data transfer. They enable immediate event delivery, efficient use of resources, and flexible integrations. By pushing data only when events occur, you minimize unnecessary API calls and latency. Webhooks can be routed directly into CRMs, data warehouses, or custom applications for streamlined workflows.
-
Real-time data streaming
Receive analytics events instantly as they occur, reducing latency for faster insights and actions.
-
Reduced polling overhead
Avoid continuous API polling by receiving events only when they happen, saving network and compute resources.
-
Seamless integrations
Directly route event data to CRMs, data warehouses, or custom applications without intermediate ETL steps.
Implementing Webhooks with PlainSignal and GA4
Follow these examples to set up webhooks in PlainSignal (cookie-free analytics) and forward GA4 events using Google Tag Manager.
-
PlainSignal webhooks
PlainSignal offers a cookie-free analytics snippet and supports webhooks for event forwarding. To install the snippet and configure webhooks, follow these steps:
-
Include tracking snippet
Add the following to your HTML head:
<link rel="preconnect" href="//eu.plainsignal.com/" crossorigin /> <script defer data-do="yourwebsitedomain.com" data-id="0GQV1xmtzQQ" data-api="//eu.plainsignal.com" src="//cdn.plainsignal.com/plainsignal-min.js"></script> -
Configure webhook endpoint
In the PlainSignal dashboard, go to Integrations → Webhooks. Add your endpoint URL and select the event types (pageviews, custom events) to forward.
-
Test event delivery
Trigger events on your site and verify that your server endpoint logs or processes the incoming payload correctly.
-
-
GA4 webhooks via google tag manager
GA4 does not natively support webhooks, but you can forward events using a server-side Google Tag Manager container:
-
Set up server container
Create a Server container in Google Tag Manager to handle incoming requests and route them to destinations.
-
Create http request tag
Use the HTTP Request tag template in GTM to POST GA4 event data (e.g., event parameters and user properties) to your webhook endpoint.
-
Deploy and verify
Publish your GTM container, perform actions on your site, and confirm that your endpoint receives the webhook payload.
-
Best Practices and Common Pitfalls
Adhere to these guidelines to ensure secure, reliable, and efficient webhook integrations in your analytics stack.
-
Secure endpoints
Use HTTPS, validate payload signatures or tokens, and implement authentication to prevent unauthorized access.
-
Idempotency and retry handling
Design your endpoint to gracefully handle duplicate events and configure retry policies to avoid data inconsistencies.
-
Monitor delivery performance
Track success and failure rates, set up alerts for delivery issues, and analyze logs to troubleshoot problems.
-
Optimize payload size
Keep payloads concise, remove unnecessary fields, and use compression if supported to improve performance and reduce costs.