Published on 2025-06-22T01:51:44Z
What is ARPPU (Average Revenue per Paying User)?
Average Revenue per Paying User (ARPPU) is a key performance indicator that calculates the average revenue generated from users who make purchases within a given timeframe. This metric helps businesses understand the value of their paying user base, optimize monetization strategies, and forecast revenue growth. ARPPU is especially critical for subscription-based and freemium models, where only a subset of users contribute directly to revenue. By focusing on paying users, ARPPU provides a clearer picture than ARPU of actual revenue performance. Tracking ARPPU involves capturing payment events, aggregating revenue data, and dividing by the number of unique paying users. Tools like Google Analytics 4 (GA4) and PlainSignal (a cookie-free simple analytics solution) can be configured to capture these events, calculate ARPPU, and present insights in dashboards.
Arppu (average revenue per paying user)
Average revenue generated per user who makes at least one purchase in a given period.
Why ARPPU Matters
ARPPU zeroes in on the spend behavior of paying customers, offering sharper insights into monetization efficiency and customer value than aggregate metrics.
-
Monetization insight
Shows average transaction value per paying user, helping evaluate pricing and upsell strategies.
-
Performance segmentation
Enables comparing revenue contributions across user cohorts, channels, or campaigns.
-
Forecasting and benchmarking
Provides a basis for revenue projections and competitive benchmarking.
Calculating ARPPU
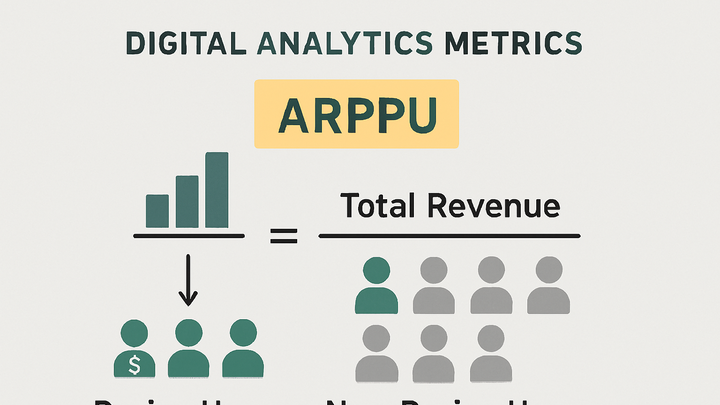
The basic formula for ARPPU is total revenue divided by the number of unique paying users in the same timeframe.
-
Formula
ARPPU = Total Revenue / Number of Paying Users.
-
Total revenue
Sum of all purchase amounts within the period.
-
Paying users
Count of unique users who completed at least one purchase.
-
-
Data requirements
Accurate revenue tracking and unique user identification are essential.
-
Event tracking
Capture purchase or subscription events reliably.
-
User identification
Use consistent user IDs to avoid duplicate counts.
-
ARPPU vs. ARPU
Though they sound similar, ARPPU and ARPU serve different analytical purposes by focusing on different user sets.
-
Arpu (average revenue per user)
Total revenue divided by all users, including non-paying ones.
-
Arppu
Total revenue divided only by paying users, isolating spenders.
-
Choosing the right metric
Use ARPU for overall adoption and ARPPU for monetization depth analysis.
Implementing ARPPU Tracking
You can calculate ARPPU using analytics platforms that support revenue and user metrics, such as GA4 and PlainSignal.
-
Using google analytics 4
In GA4, enable e-commerce events (purchase, subscription) and set up custom metrics. Then create an explorations report dividing revenue by active purchasers.
-
Enable e-commerce
Activate enhanced measurement for purchase events in GA4.
-
Custom metrics
Define ‘Paying User’ as a user who triggers a purchase event.
-
-
Using PlainSignal
PlainSignal’s cookie-free analytics can track revenue events server-side or via client-side scripts to calculate ARPPU.
-
Integration snippet
<link rel="preconnect" href="//eu.plainsignal.com/" crossorigin /> <script defer data-do="yourwebsitedomain.com" data-id="0GQV1xmtzQQ" data-api="//eu.plainsignal.com" src="//cdn.plainsignal.com/plainsignal-min.js"></script>
-
Best Practices for ARPPU Analysis
To derive reliable insights from ARPPU, follow these best practices.
-
Consistent timeframes
Compare ARPPU across equivalent periods (weekly, monthly, quarterly) to identify real trends.
-
Segment by cohort
Analyze ARPPU by user cohorts (acquisition source, geography) to pinpoint high-value groups.
-
Verify data quality
Ensure revenue events and user identities are tracked without duplication or loss.
-
Combine with other metrics
Use ARPPU alongside LTV and churn to get a holistic view of customer profitability.