Published on 2025-06-22T09:52:38Z
What is a Top Conversion Path? Examples of Top Conversion Paths
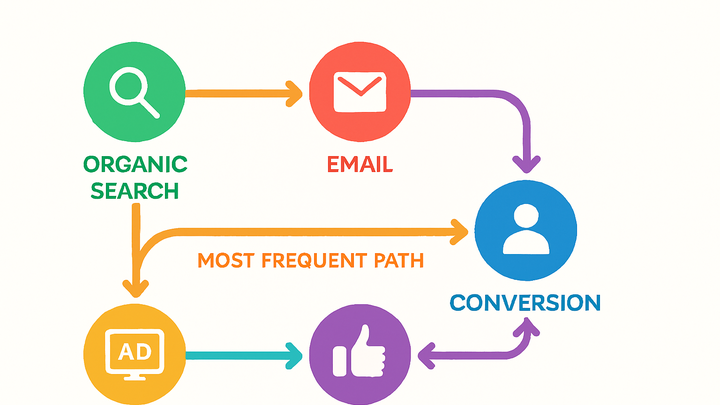
Top Conversion Path is the most common sequence of marketing touchpoints a user encounters before completing a desired action, such as a purchase or signup. It provides a holistic view of the customer journey across channels and devices. Understanding top paths is crucial for informed attribution modeling, allowing marketers to assign credit fairly to each interaction. This insight helps optimize marketing spend, improve user experience, and increase conversion rates.
Top conversion path
The most frequent sequence of user touchpoints leading to a conversion, used for attribution and optimizing marketing channels.
Definition and Importance
A Top Conversion Path is the most common sequence of marketing touchpoints that lead a user to complete a desired action, such as a purchase or signup. It provides a holistic view of the customer journey across channels and devices. Understanding top paths is crucial for informed attribution modeling, allowing marketers to assign credit fairly to each interaction. This insight helps optimize marketing spend, improve user experience, and increase conversion rates.
-
Definition
The sequence of touchpoints a user follows before converting, ranked by frequency.
-
Why it matters
Analyzing top paths uncovers which channels or campaigns drive conversions most effectively.
-
Marketing optimization
Allocate budget to channels that appear most often in top conversion paths.
-
Attribution accuracy
Select or adjust attribution models based on observed user journeys.
-
Key Components
Top conversion paths consist of several elements: individual touchpoints, the order of interactions, and the timing between them. Each component offers unique insights into user behavior, from initial discovery to final conversion.
-
Touchpoints
Interactions such as organic search, paid ads, email clicks, or direct visits that users have with your brand.
-
Paid vs. organic
Distinguish interactions from paid campaigns versus organic sources.
-
Cross-device touches
Users may switch devices; group interactions across mobile, desktop, and tablet.
-
-
Sequence and timing
The chronological order of touchpoints and the time intervals between them.
-
Path order
Position of each touch in the overall sequence.
-
Time lag
Elapsed time between the first and last interaction.
-
Tracking with PlainSignal and GA4
Capturing top conversion paths requires proper implementation in your analytics tools. Below are steps for using PlainSignal and Google Analytics 4 to record and analyze user journeys.
-
PlainSignal (cookie-free analytics)
PlainSignal tracks user paths without third-party cookies, preserving privacy while providing path data.
-
Insert tracking script
Copy and paste the following before the closing </head> tag:
<link rel="preconnect" href="//eu.plainsignal.com/" crossorigin /> <script defer data-do="yourwebsitedomain.com" data-id="0GQV1xmtzQQ" data-api="//eu.plainsignal.com" src="//cdn.plainsignal.com/plainsignal-min.js"></script> -
View path reports
In the PlainSignal dashboard, go to Conversion Paths to explore and filter user journeys.
-
-
Google analytics 4 (GA4)
GA4 includes a Path Exploration feature for deep dives into user journeys.
-
Enable path exploration
Navigate to Explore > Path exploration, then set a start or end event to generate the path report.
-
Analyze nodes and flows
Each node represents an event or channel; use the visualization to identify dominant paths and drop-offs.
-
Best Practices
Use the following strategies to maximize insights from top conversion path analysis and improve marketing performance.
-
Segment your paths
Break down conversion paths by user characteristics or traffic sources for targeted analysis.
-
Demographic segments
Compare paths across age groups, locations, or device types.
-
Behavioral segments
Analyze differences between new vs. returning users or high-value customers.
-
-
Review attribution models regularly
Adjust attribution settings to reflect actual path data and business goals.
-
Test model variations
Experiment with first-touch, last-touch, linear, or data-driven models.
-
Measure performance impact
Track how model changes influence campaign ROI and budget allocation.
-