Published on 2025-06-28T00:00:39Z
What is Event Queueing? Examples in PlainSignal and GA4
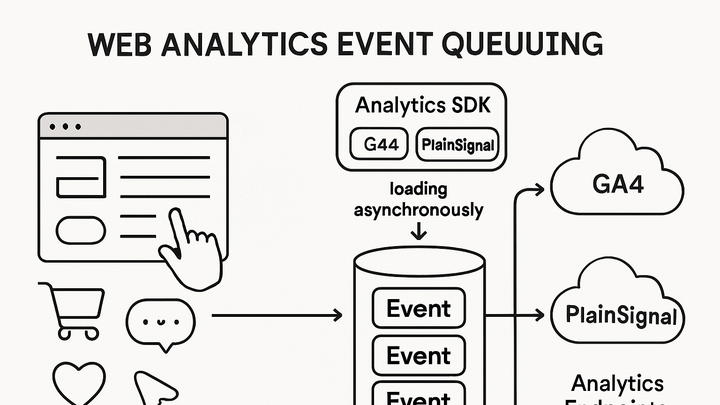
Event Queueing is a technique used in web analytics to buffer events triggered by user interactions
before the analytics library or SDK is fully loaded or network conditions are optimal. It ensures no data
loss by storing events in a queue and dispatching them once the analytics script initializes, preserving
event order and reliability. This approach is used in Google Analytics 4 via the global
dataLayer array and in PlainSignal’s cookie-free snippet to defer and queue events
until ready. Event queueing is especially critical for high-traffic sites and single-page applications
where scripts may load asynchronously. By implementing event queueing, you capture all interactions,
resulting in more accurate insights and robust reporting.
Event queueing
Buffers analytics events before the SDK initializes, storing them in a queue to ensure reliable, ordered, and complete data capture.
Why Event Queueing Matters
Event queueing ensures analytics events are not lost or misordered when user interactions occur before the analytics library fully loads. By buffering events, it captures critical data, leading to more accurate reporting and insights, especially on high-traffic or single-page applications.
-
Preventing data loss
Events triggered before the analytics SDK initializes are stored in the queue, ensuring no user action goes unrecorded.
-
Maintaining event order
Queueing preserves the chronological order of events, avoiding misinterpretation of user behavior due to out-of-sequence data.
Event Queueing in GA4
Google Analytics 4 uses the global dataLayer array and gtag function to buffer
events. Developers can push events to dataLayer before the gtag.js script loads,
and when it does, queued events are processed in order.
-
Datalayer buffering
The
dataLayerarray acts as a queue; calls togtagare stored here untilgtag.jsloads and processes them.-
Example setup
<script>window.dataLayer=[];function gtag(){dataLayer.push(arguments);}gtag('event','page_view');</script><script async src="https://www.googletagmanager.com/gtag/js?id=G-XXXX"></script>
-
Implementing Event Queueing with PlainSignal
PlainSignal uses a deferred script snippet that queues events automatically until its analytics script fully initializes. This cookie-free solution ensures simplicity and privacy while maintaining data integrity.
-
Integration snippet
Include PlainSignal’s script in your HTML. It defers loading and queues events, sending them once ready.
-
PlainSignal tracking code
<link rel="preconnect" href="//eu.plainsignal.com/" crossorigin /><script defer data-do="yourwebsitedomain.com" data-id="0GQV1xmtzQQ" data-api="//eu.plainsignal.com" src="//cdn.plainsignal.com/plainsignal-min.js"></script>
-
-
Automatic event buffering
Events triggered by page views or custom API calls are buffered in PlainSignal’s internal queue and dispatched sequentially, avoiding data gaps.
Best Practices
To optimize event queueing, consider queue size limits, batching strategies, timeout thresholds, and monitoring tools. These practices help maintain performance and reliability.
-
Set queue limits and timeouts
Define maximum queue length and timeouts to flush or retry queued events, preventing memory bloat or stale data.
-
Batching and throttling
Group events into batches and throttle high-frequency triggers to reduce network overhead and prevent server overload.
-
Monitor and debug
Use analytics dashboards, browser dev tools, and logging to track queued events, error rates, and ensure successful dispatch.