Published on 2025-06-28T04:32:36Z
What are User Segments? Examples for User Segments
User Segments are subsets of an analytics user base grouped by shared characteristics, behaviors, or attributes. By dividing visitors into meaningful groups—such as new vs returning users, geographic regions, device types, or engagement patterns—analysts gain deeper insights into how different audiences interact with a product. In analytics platforms like Google Analytics 4 (GA4) and PlainSignal, segments enable targeted analysis, helping to optimize marketing strategies, personalize experiences, and improve retention. With GA4, segments can be created based on events, user properties, or demographics, while PlainSignal offers a lightweight, cookie-free approach that leverages custom event tracking and dashboard filters. Effective segmentation empowers data-driven decisions by revealing patterns that might be obscured in aggregate metrics. Properly defined segments drive focused A/B tests, tailored messaging, and more efficient resource allocation.
User segments
Subsets of users grouped by shared attributes or behaviors, enabling targeted analysis, personalization, and optimized marketing strategies.
Definition and Significance
This section introduces what user segments are and why they matter for deriving actionable insights from analytics data.
-
Definition of user segments
User segments are groups of users classified by common characteristics, such as demographics, behaviors, or technical attributes, to enable focused analysis.
-
User attributes
Characteristics like age, gender, or location used to categorize users into meaningful groups.
-
Behavioral attributes
Actions and interactions such as page views, session duration, and conversion events that define user behavior patterns.
-
-
Why segmentation matters
Segmenting users allows you to tailor experiences, measure specific behaviors, and compare performance across different audiences.
-
Personalization
Deliver customized content and messages to distinct user groups based on their preferences and history.
-
Optimization
Allocate marketing and development resources effectively by focusing on high-value segments.
-
Common Segmentation Criteria
Overview of popular attributes and behaviors used to create user segments for deeper analysis.
-
Demographic segmentation
Based on inherent user characteristics that are typically static or slowly changing.
-
Age
Grouping users into age brackets (e.g., 18–24, 25–34) to tailor age-appropriate content.
-
Location
Segmenting by country, region, or city to address local needs and preferences.
-
-
Behavioral segmentation
Based on user interactions with your site or app.
-
Engagement level
Using metrics like session duration and pages per session to identify highly engaged users.
-
Purchase history
Grouping users by past purchases, cart abandons, or subscription status.
-
-
Acquisition source
Based on how users discovered your site, such as organic search, paid ads, or referrals.
-
Traffic source
Identifying segments from search engines, social media, email campaigns, and referrals.
-
Utm campaigns
Isolating users acquired through specific marketing campaigns using UTM parameters.
-
-
Technographic segmentation
Based on the technology users use to access your site or app.
-
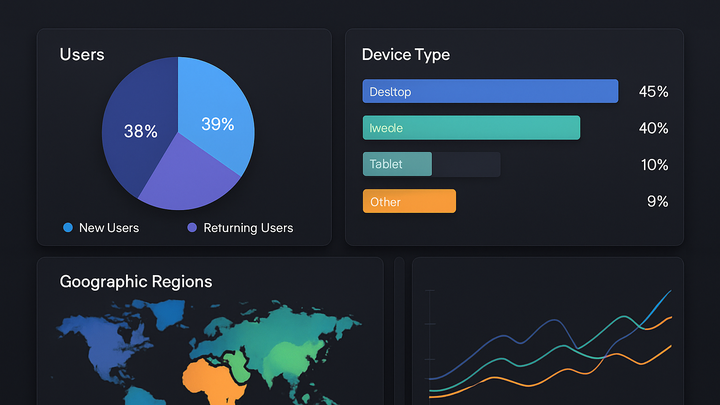
Device type
Segmenting by mobile, desktop, or tablet to optimize device-specific experiences.
-
Browser & os
Grouping users by browser (Chrome, Safari) or operating system for compatibility testing.
-
Implementing User Segments in Analytics Tools
Step-by-step guidance for configuring and applying user segments in GA4 and PlainSignal.
-
Google analytics 4 (GA4)
In GA4, you can create and apply user segments to filter reports or within Explorations.
-
Navigate to explore
Open GA4 and click ‘Explore’ in the left-hand menu to start a free-form analysis.
-
Create a user segment
In the Variables pane, click ‘Segments’ → ‘New segment’ → choose ‘User segment’ and set conditions such as event count or user property.
-
Apply the segment
Drag the segment into your analysis or apply it to report filters to view data for that specific group.
-
-
PlainSignal
PlainSignal offers a cookie-free analytics approach where you can define and filter segments using custom event properties and dashboard filters.
-
Add tracking snippet
Paste the PlainSignal code into your site’s
<head>:<link rel="preconnect" href="//eu.plainsignal.com/" crossorigin /> <script defer data-do="yourwebsitedomain.com" data-id="0GQV1xmtzQQ" data-api="//eu.plainsignal.com" src="//cdn.plainsignal.com/plainsignal-min.js"></script> -
Filter by properties
In the PlainSignal dashboard, use filters on URL, referrer, or custom event properties to isolate user segments without cookies.
-
Best Practices for User Segmentation
Guidelines to create meaningful, actionable, and sustainable user segments.
-
Align with business objectives
Ensure each segment addresses a clear goal or question aligned with your business strategy.
-
Define objectives
Start with specific questions you need to answer, such as boosting retention or improving onboarding.
-
Limit segment count
Focus on key segments to avoid over-segmentation and analysis complexity.
-
-
Maintain clarity and consistency
Use precise, non-overlapping definitions to keep your segments clean and comparable over time.
-
Use clear conditions
Avoid vague criteria; be specific about event names, property values, or thresholds.
-
Review regularly
Audit and update segments periodically as your product and user base evolve.
-
-
Validate with qualitative insights
Combine quantitative segments with qualitative research for richer understanding.
-
User interviews
Talk to representative users to validate assumptions about each segment.
-
Feedback surveys
Use in-app or email surveys to gather direct feedback from segment members.
-